Answer to Question 1
ANS:
Toxins such as mercury become more concentrated in animals and in people high in the food chain. Because of bioaccumulation, large game fish at the top of the aquatic food chain (such as tilefish, swordfish, king mackerel, and shark) generally have the highest concentrations of mercury (10 times the average). Consumers who enjoy eating these fish should select the smaller, younger ones (within legal limits). Also because of bioaccumulation, the concentrations in fish may be a million times higher than the concentrations in the water itself.
The EPA regulates commercial fishing to help ensure that fish destined for consumption in the United States meet safety standards for mercury and other contaminants. Farm-raised fish usually have lower concentrations of mercury than fish caught in the wild. Consequently, most consumers in the United States are not in danger of receiving harmful levels of mercury from fish.
The potential harm from contaminants must be balanced against the potential benefits from nutrients. Pregnant and lactating women and young children are most vulnerable because mercury toxicity damages the developing brain. Yet they are also likely to benefit from consuming seafood rich in omega-3 fatty acids. To receive the benefits and minimize the risks, the FDA advises that pregnant and lactating women and young children can safely consume up to 12 ounces of a variety of seafood per week. Commonly eaten choices that are relatively low in mercury include shrimp, canned light tuna, salmon, pollock, and catfish. In addition, albacore (white) tuna should be limited to 6 ounces per week and large predatory fish (tilefish, swordfish, king mackerel, and shark) should be avoided altogether. Although limiting seafood during pregnancy is advisable, such a strategy may have a relatively small effect on prenatal blood mercury levels.
What about the noncommercial fish a person catches from a local lake, river, or ocean? After all, it's almost impossible to tell whether water is contaminated without sophisticated equipment. Each state monitors its waters and issues advisories to inform the public if chemical contaminants have been found in the local fish. To find out whether a fish advisory has been posted in your region, call the local or state environmental health department.
All things considered, fish continue to support a healthy diet, providing valuable protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and minerals. For most adults, the benefits of protecting against heart disease outweigh the risks of consuming seafood regularly. Ideally, consumers would select fish with high levels of omega-3 fatty acids and low levels of mercury, such as anchovies, herring, lake trout, mackerel, pollock, salmon, sardines, smelt, and tilapia. In addition, they should select a variety of seafood to reduce the risk of exposure to contaminants from a single source.
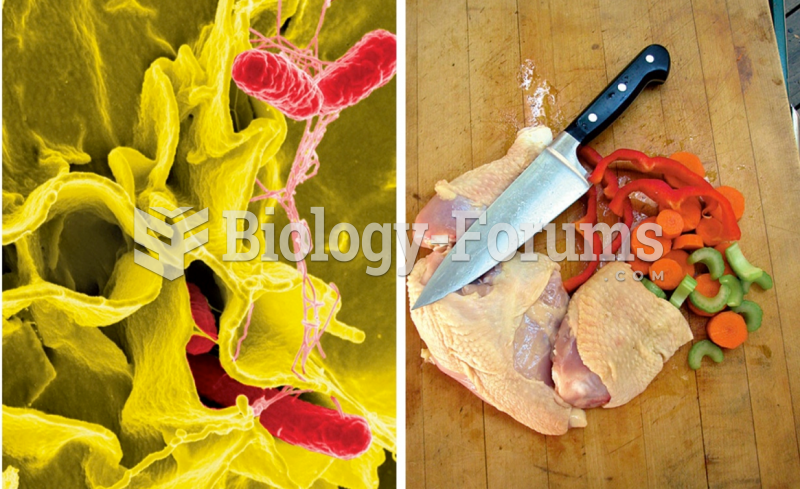
Answer to Question 2
ANS:
Avoid cross-contamination by keeping raw eggs, meat, poultry, and seafood separate from other foods. Wash all utensils and surfaces (such as cutting boards or platters) that have been in contact with these foods with hot, soapy water before using them again. Bacteria inevitably left on the surfaces from the raw meat can recontaminate the cooked meat or other foodsa problem known as cross-contamination. Washing raw eggs, meat, and poultry is not recommended because the extra handling increases the risk of cross-contamination