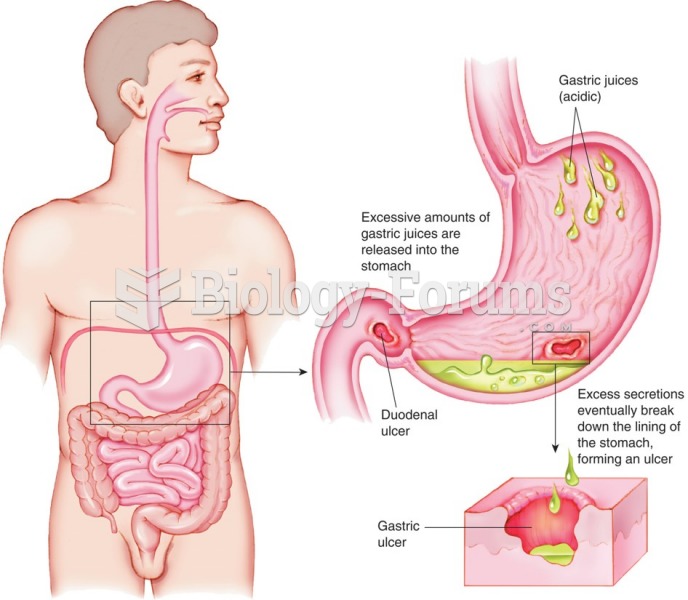
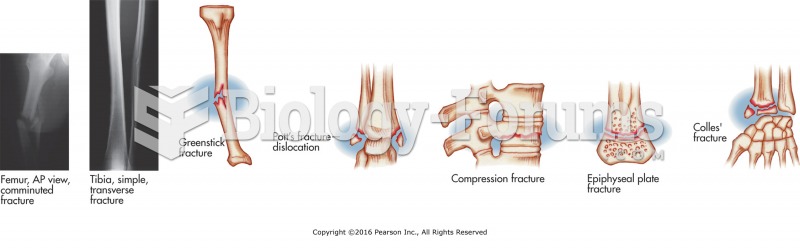
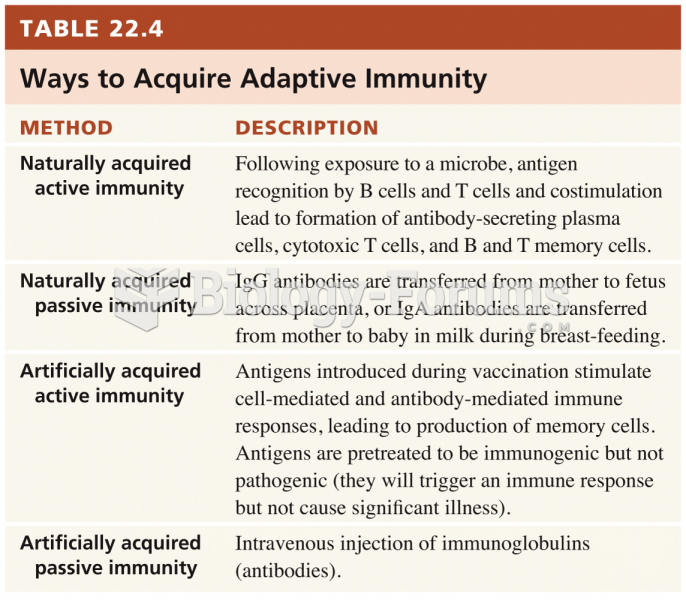
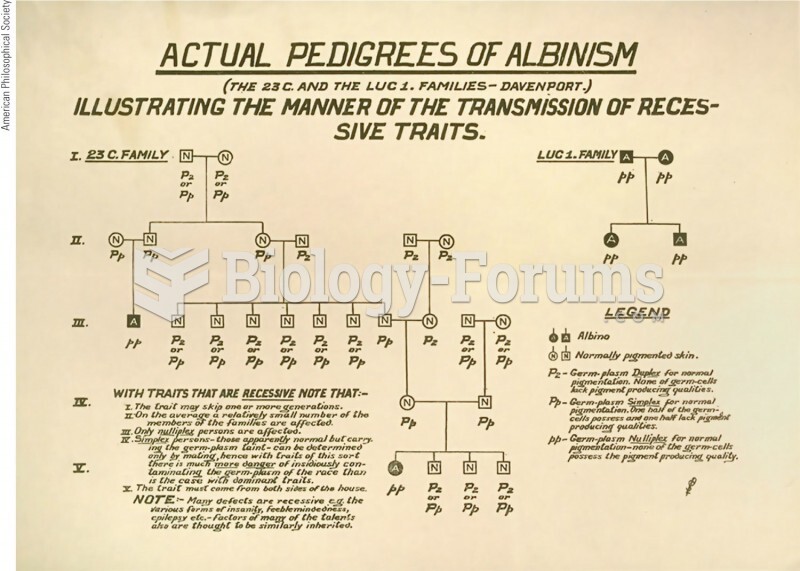
|
|
|
The top five reasons that children stay home from school are as follows: colds, stomach flu (gastroenteritis), ear infection (otitis media), pink eye (conjunctivitis), and sore throat.
In the ancient and medieval periods, dysentery killed about ? of all babies before they reach 12 months of age. The disease was transferred through contaminated drinking water, because there was no way to adequately dispose of sewage, which contaminated the water.
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.
The liver is the only organ that has the ability to regenerate itself after certain types of damage. As much as 25% of the liver can be removed, and it will still regenerate back to its original shape and size. However, the liver cannot regenerate after severe damage caused by alcohol.
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.