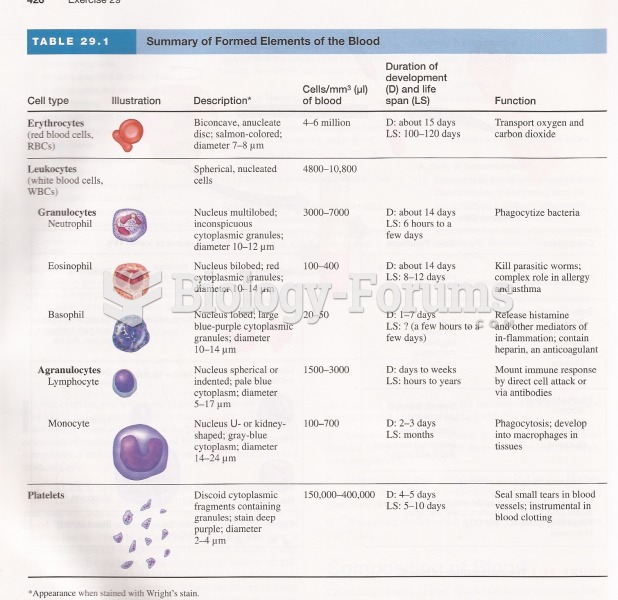
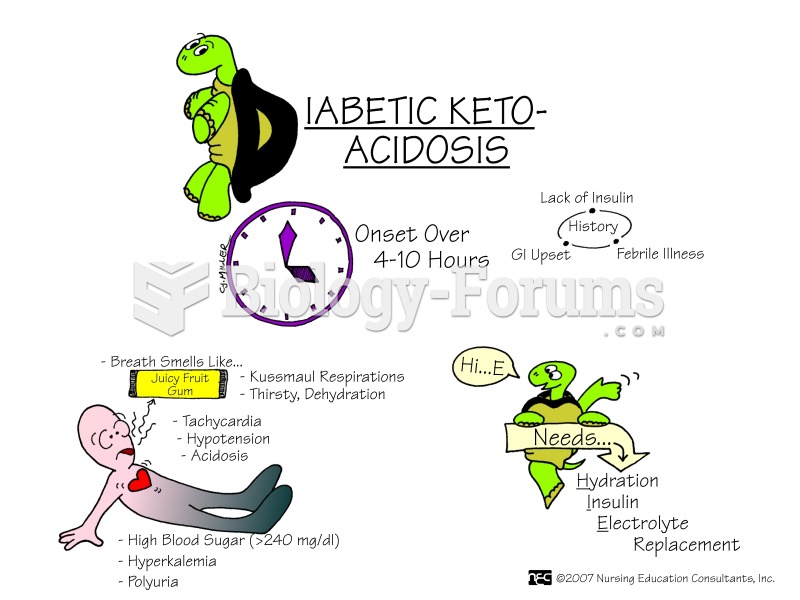
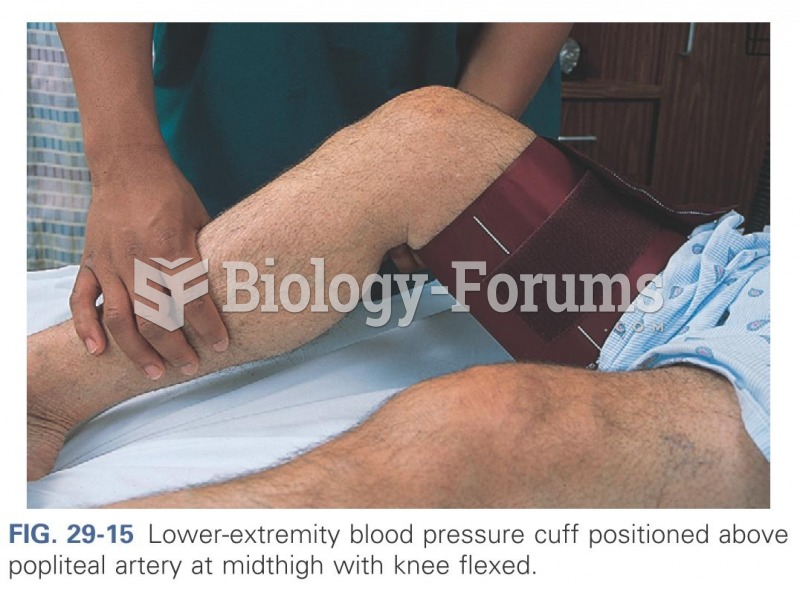
|
|
|
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
Though “Krazy Glue” or “Super Glue” has the ability to seal small wounds, it is not recommended for this purpose since it contains many substances that should not enter the body through the skin, and may be harmful.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
An identified risk factor for osteoporosis is the intake of excessive amounts of vitamin A. Dietary intake of approximately double the recommended daily amount of vitamin A, by women, has been shown to reduce bone mineral density and increase the chances for hip fractures compared with women who consumed the recommended daily amount (or less) of vitamin A.