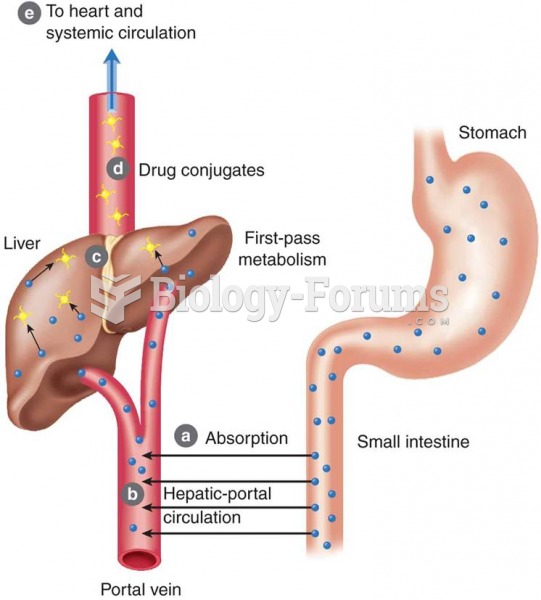
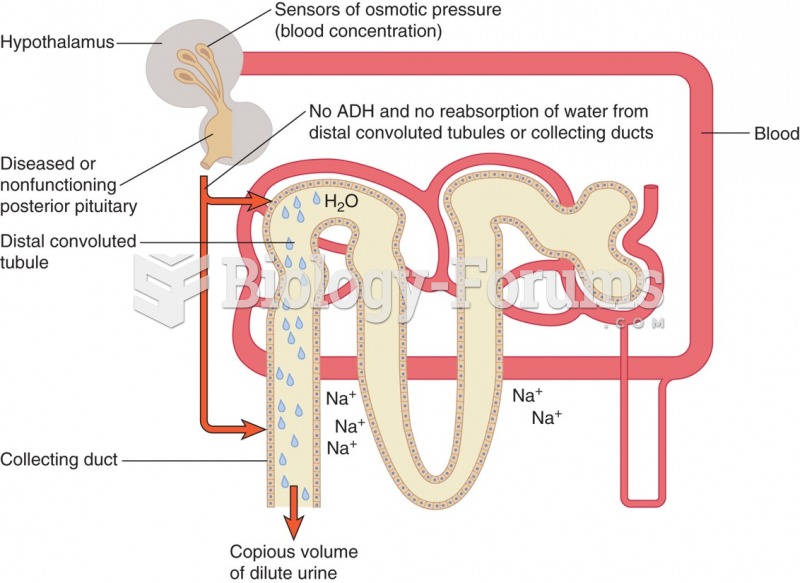
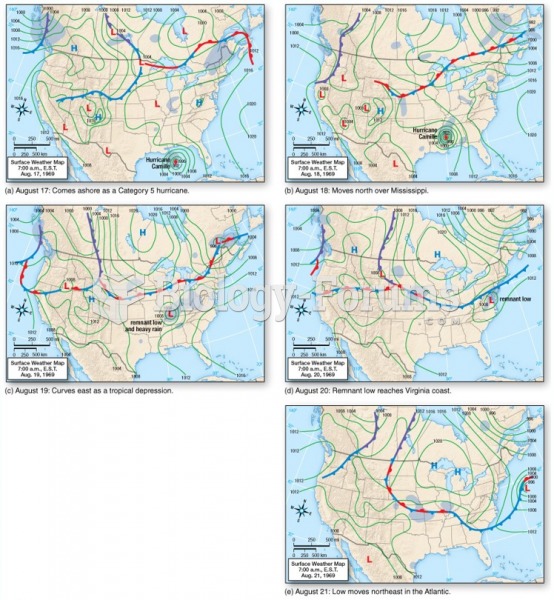
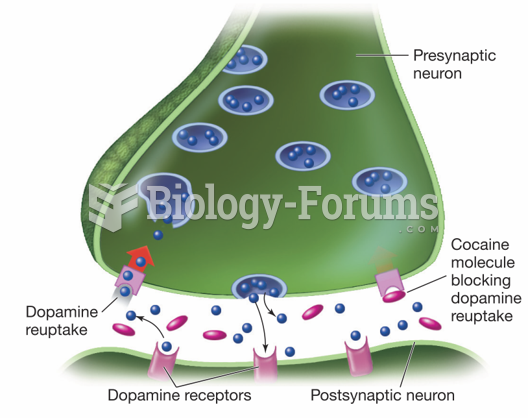
|
|
|
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, lung disease is the third leading killer in the United States, responsible for one in seven deaths. It is the leading cause of death among infants under the age of one year.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Risperdal, an adult antipsychotic drug, for the symptomatic treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism. The approval is the first for the use of a drug to treat behaviors associated with autism in children. These behaviors are included under the general heading of irritability and include aggression, deliberate self-injury, and temper tantrums.