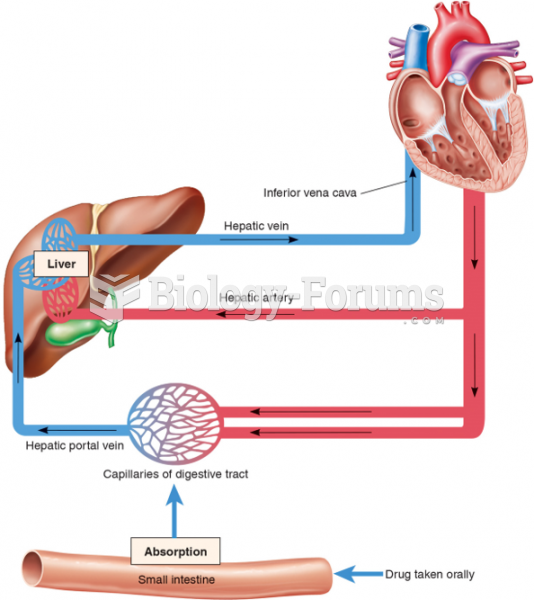
Answer to Question 1
Alcohol is toxic to the brain, and therefore we speak of people who have ingested a large amount of alcohol as intoxicated. People in all cultures drink alcohol, and thus the negative effects of alcohol on the brain are widespread throughout the world. Acute alcohol intoxication disables the hippocampus, which can destroy the ability of an individual to learn or memorize data, or learn from experience. Thus it is futile to try to discuss issues or ideas with an intoxicated individual.
Chronic alcohol use is even more dangerous than acute alcohol intoxication. Individuals who chronically abuse alcohol may experience the following adverse consequences:
The frontal lobes may deteriorate, which impairs the person's ability to process information and thus make informed decisions.
Liver damage (sclerosis of the liver) may destroy the body's ability to metabolize vitamin B (thiamine).
Vitamin B deficiency diminishes the function of neurons and glial cells; damages the body's ability to process iron; and reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Chronic anemia can cause permanent brain damage.
Alzheimer's disease may develop in people who are genetically predisposed to this condition at twice the rate of the population.
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is the ultimate result of a thiamine deficiency. This syndrome causes permanent dementia characterized by confusion, confabulation, memory loss, an inability to develop new memories, and various motor signs such as nystagmus and ataxia.
Answer to Question 2
The role of a muscle spindle (named due to its spindle shape) is to supply information to the neuromuscular system about muscle length. It also provides feedback concerning motion and position. Muscle spindles are innervated by afferent and efferent systems. The afferent component communicates the sense of muscle change to the central nervous system (CNS). The efferent component sends nerve impulses that result in contraction of the intrafusal fibers. Intrafusal fibers are attached to muscles and can sense changes in the length of a muscle.