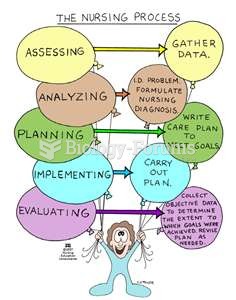
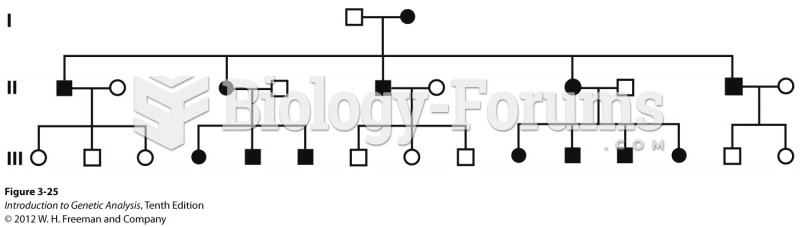
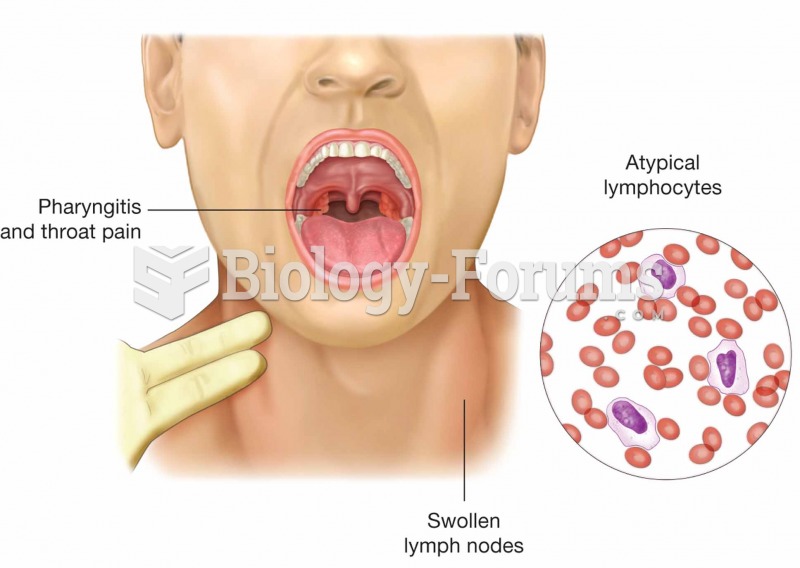
|
|
|
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.