|
|
|
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. As of yet, there is no cure. Everyone is at risk, and there may be no warning signs. It is six to eight times more common in African Americans than in whites. The best and most effective way to detect glaucoma is to receive a dilated eye examination.
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
ACTH levels are normally highest in the early morning (between 6 and 8 A.M.) and lowest in the evening (between 6 and 11 P.M.). Therefore, a doctor who suspects abnormal levels looks for low ACTH in the morning and high ACTH in the evening.
 When using an interpreter, the nurse should pose questions directly to the patient, not the interpre
When using an interpreter, the nurse should pose questions directly to the patient, not the interpre
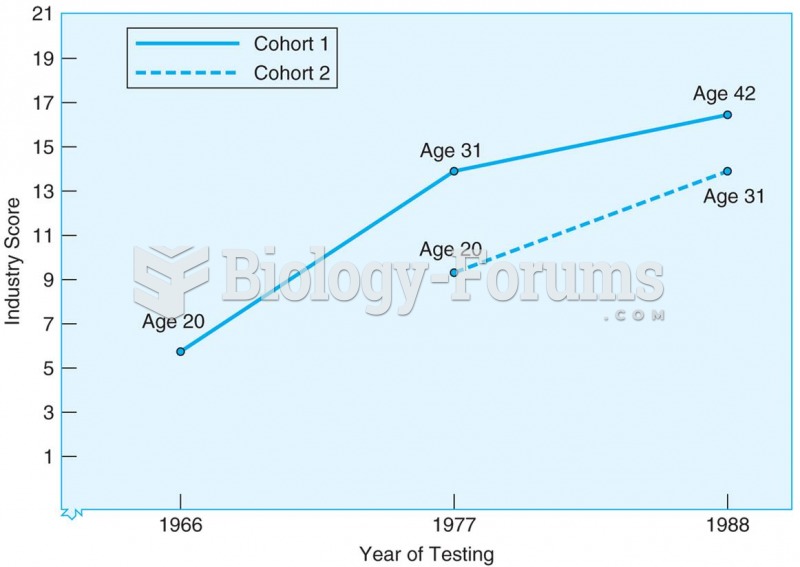 Results from sequential study of two cohorts tested at three ages and at three different points in t
Results from sequential study of two cohorts tested at three ages and at three different points in t