|
|
|
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
As of mid-2016, 18.2 million people were receiving advanced retroviral therapy (ART) worldwide. This represents between 43–50% of the 34–39.8 million people living with HIV.
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
Disorders that may affect pharmacodynamics include genetic mutations, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's disease, and certain forms of insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus.
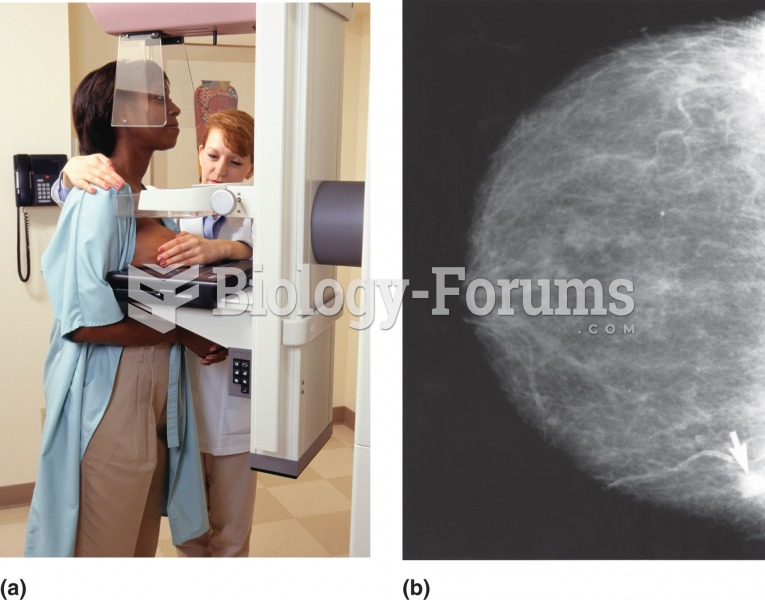 Mammography. (a) A health-care professional assists the patient to ensure the breast is placed ideal
Mammography. (a) A health-care professional assists the patient to ensure the breast is placed ideal
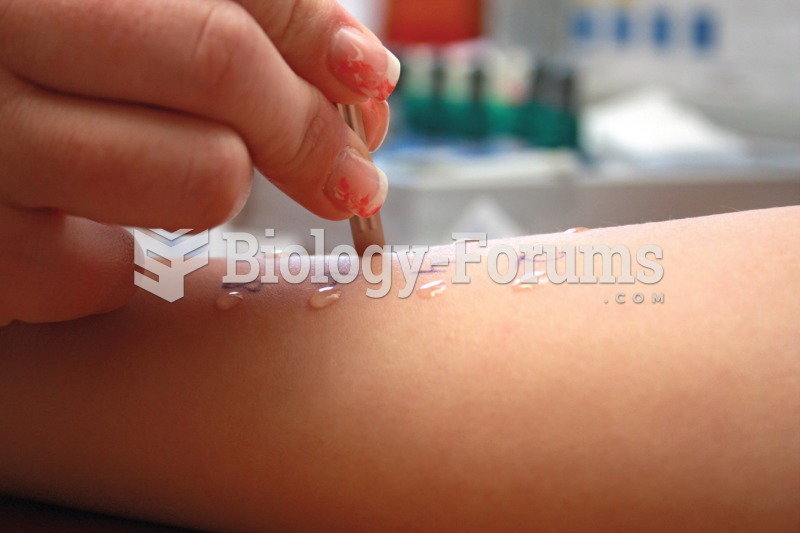 The patient is undergoing an allergy skin test by receiving subdermal inoculations of allergens. Inf
The patient is undergoing an allergy skin test by receiving subdermal inoculations of allergens. Inf





