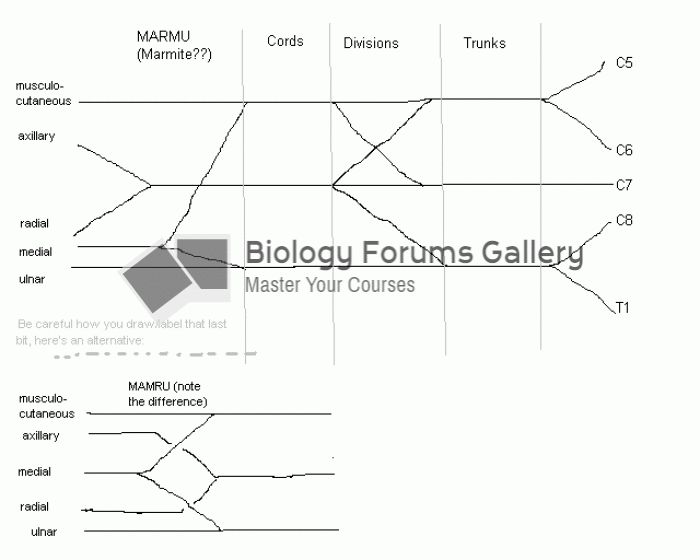
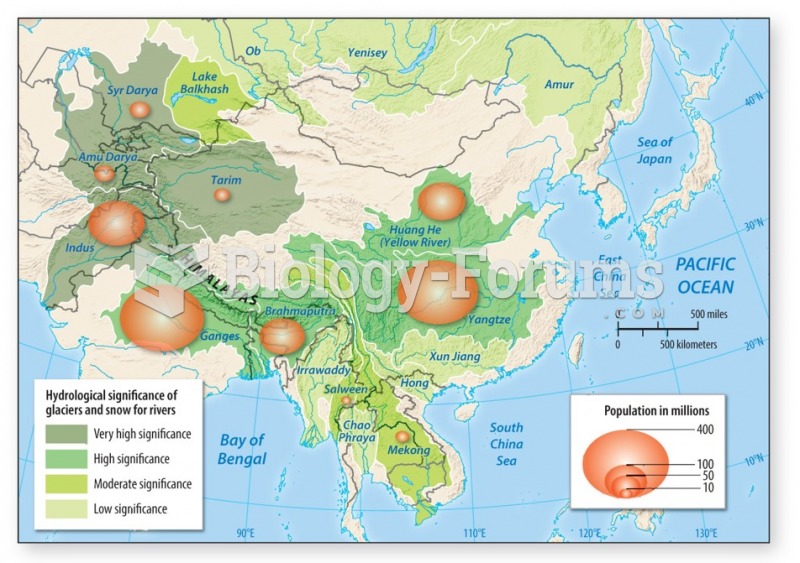
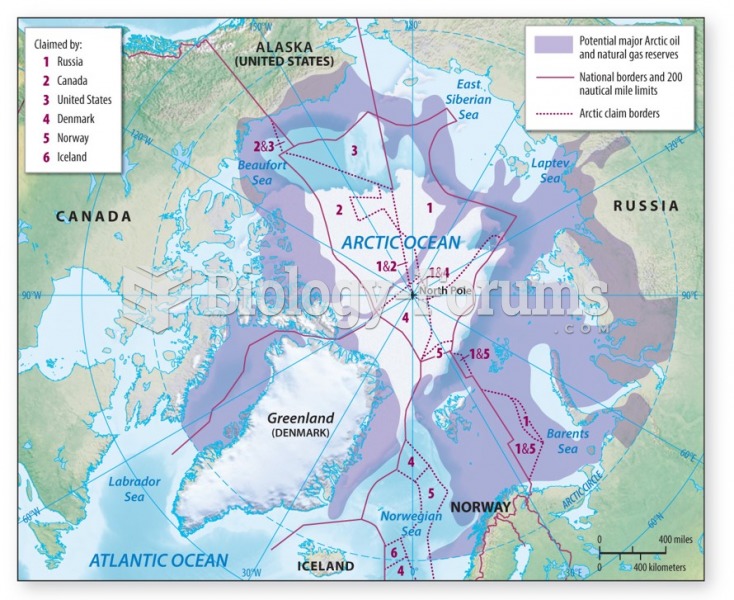
|
|
|
This year, an estimated 1.4 million Americans will have a new or recurrent heart attack.
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
An identified risk factor for osteoporosis is the intake of excessive amounts of vitamin A. Dietary intake of approximately double the recommended daily amount of vitamin A, by women, has been shown to reduce bone mineral density and increase the chances for hip fractures compared with women who consumed the recommended daily amount (or less) of vitamin A.
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.