|
|
|
Eating food that has been cooked with poppy seeds may cause you to fail a drug screening test, because the seeds contain enough opiate alkaloids to register as a positive.
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
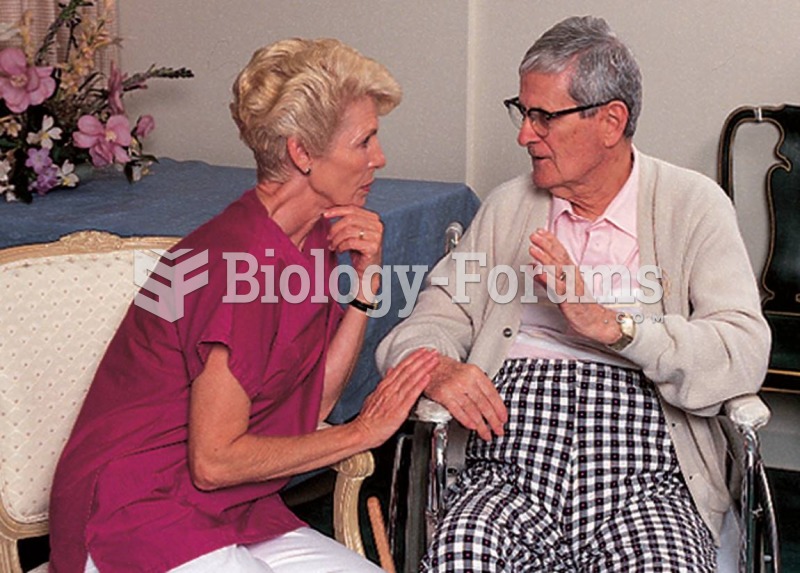
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.