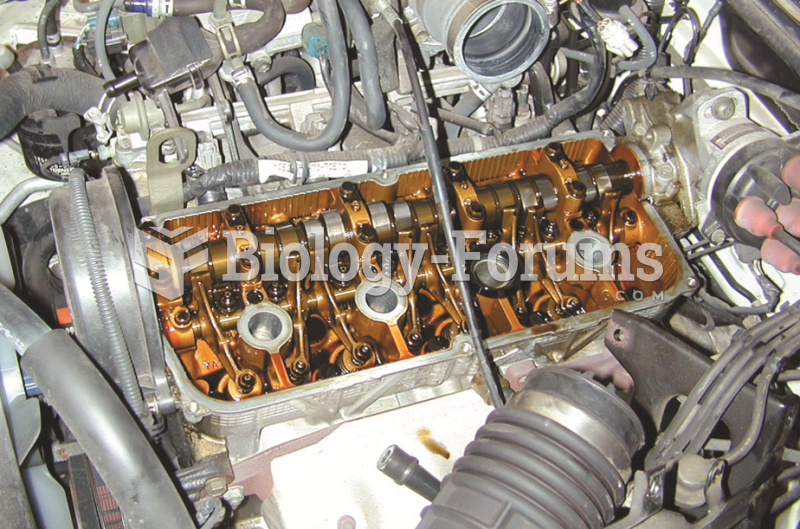
|
|
|
Children of people with alcoholism are more inclined to drink alcohol or use hard drugs. In fact, they are 400 times more likely to use hard drugs than those who do not have a family history of alcohol addiction.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.