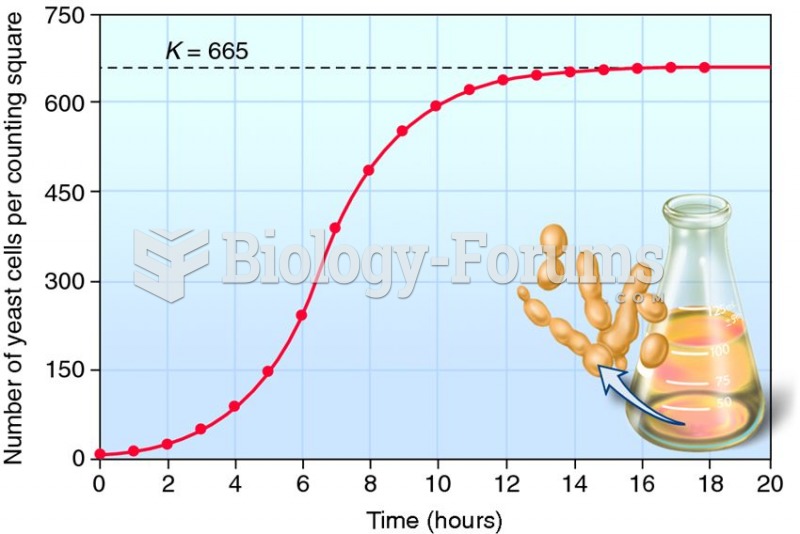
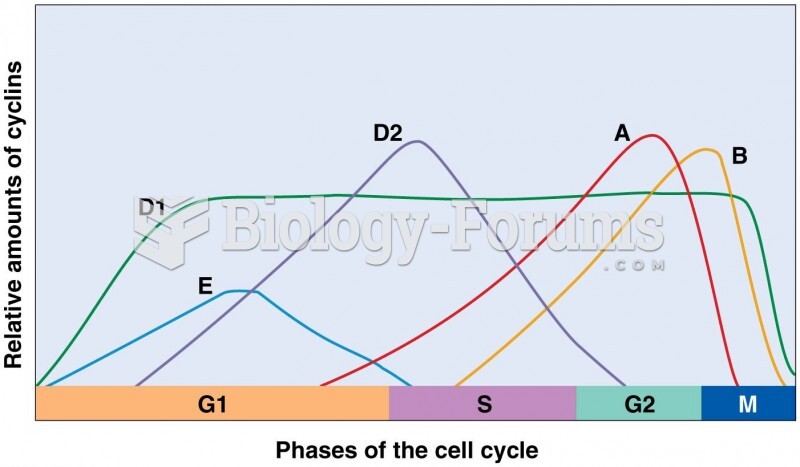
|
|
|
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.