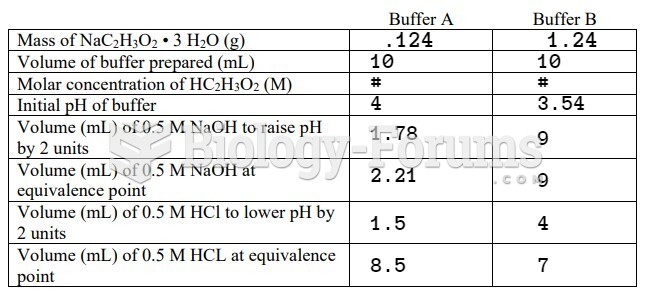
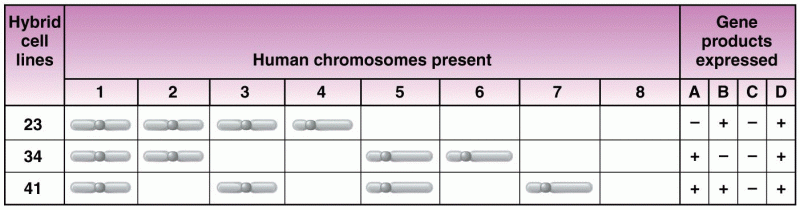
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Did you know?
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
Did you know?
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
Did you know?
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
Did you know?
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.