This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Though “Krazy Glue” or “Super Glue” has the ability to seal small wounds, it is not recommended for this purpose since it contains many substances that should not enter the body through the skin, and may be harmful.
Did you know?
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.
Did you know?
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Did you know?
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.
Did you know?
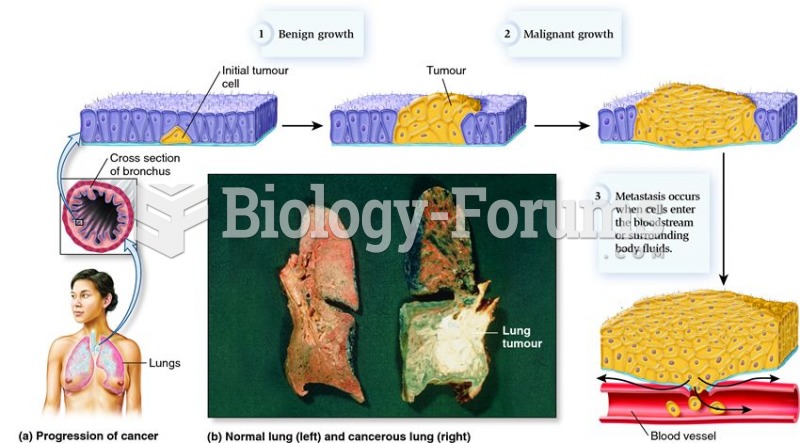
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.