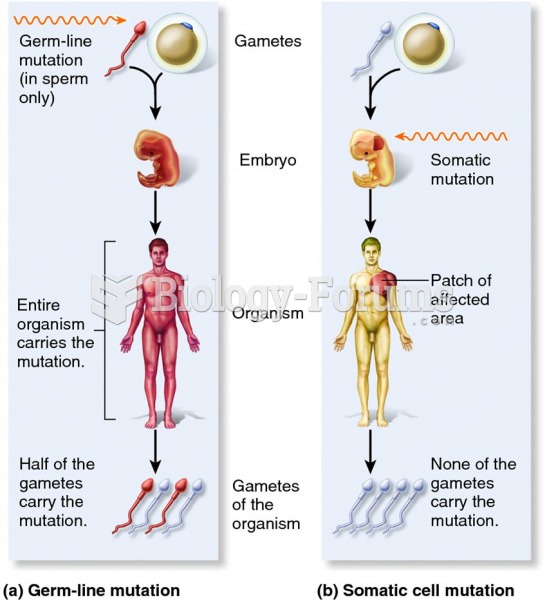
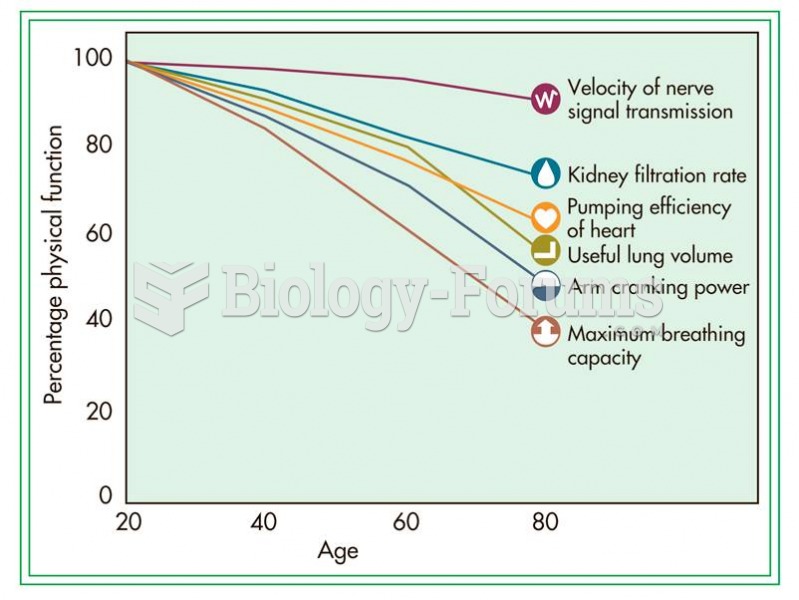
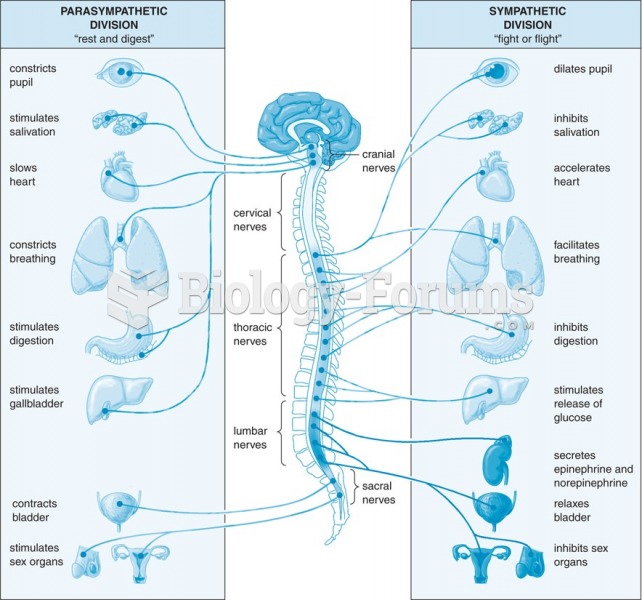
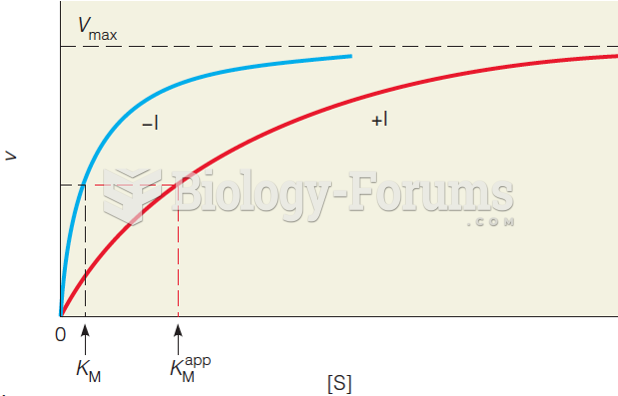
|
|
|
Did you know?
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.
Did you know?
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Did you know?
It is widely believed that giving a daily oral dose of aspirin to heart attack patients improves their chances of survival because the aspirin blocks the formation of new blood clots.
Did you know?
Human stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve small pieces of metal such as razor blades or staples.
Did you know?
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.