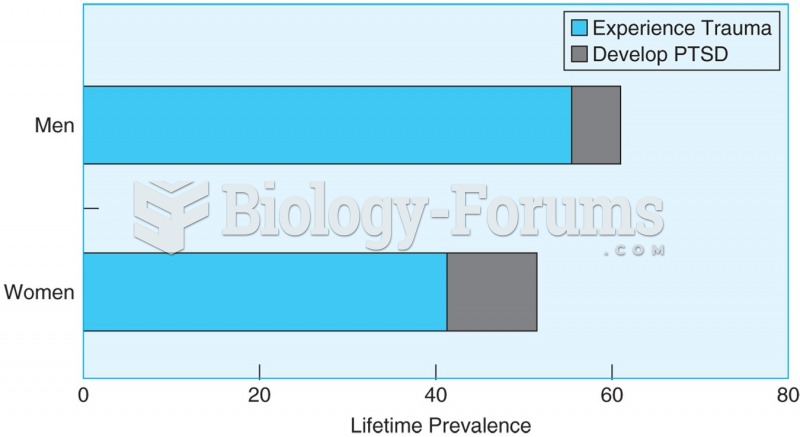
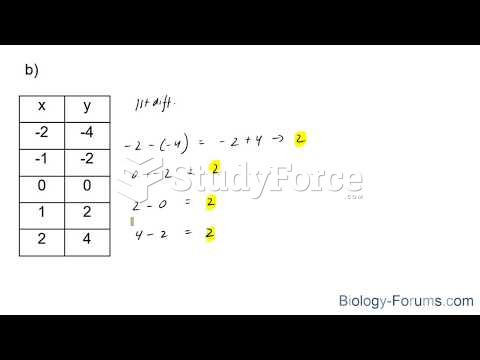
|
|
|
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
Atropine, along with scopolamine and hyoscyamine, is found in the Datura stramonium plant, which gives hallucinogenic effects and is also known as locoweed.
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.