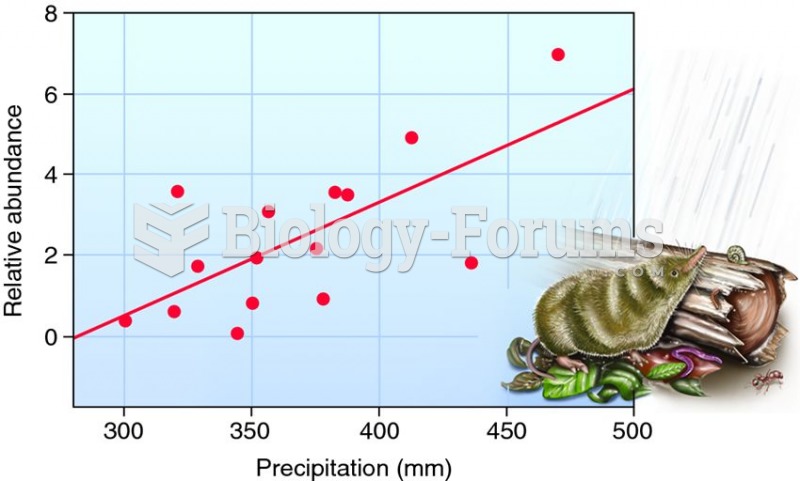
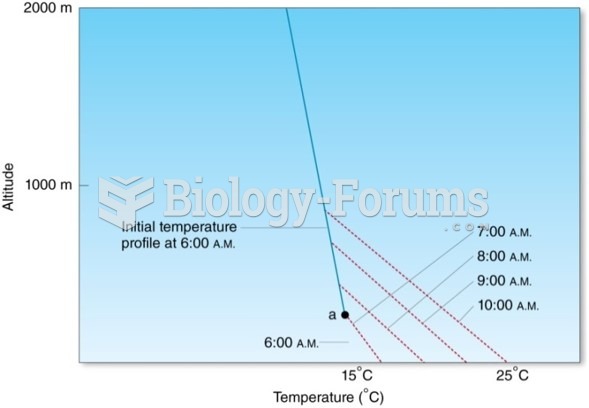
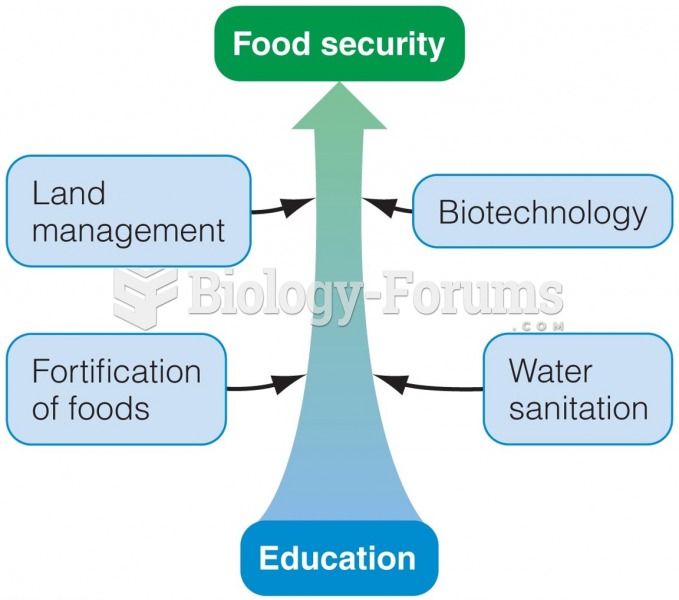
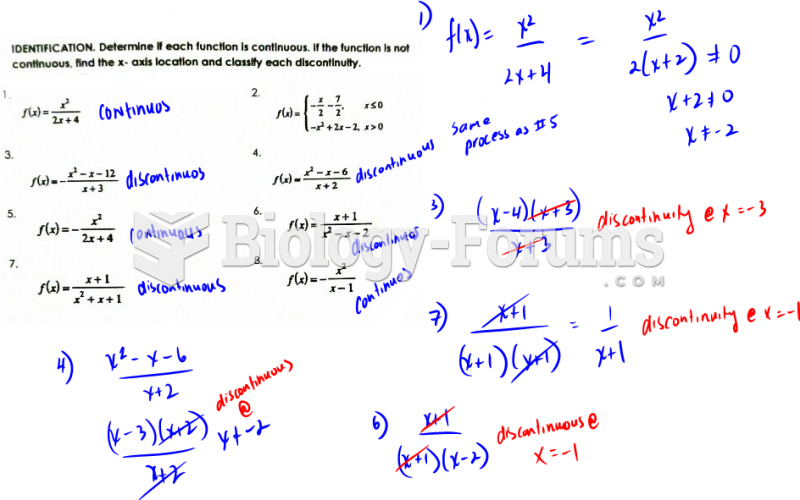
|
|
|
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
The most common childhood diseases include croup, chickenpox, ear infections, flu, pneumonia, ringworm, respiratory syncytial virus, scabies, head lice, and asthma.
The first oral chemotherapy drug for colon cancer was approved by FDA in 2001.