|
|
|
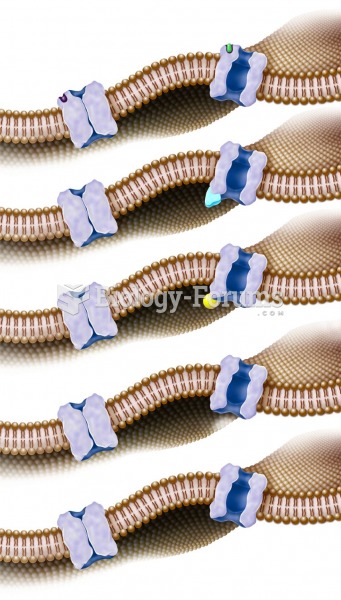
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Medication errors are more common among seriously ill patients than with those with minor conditions.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
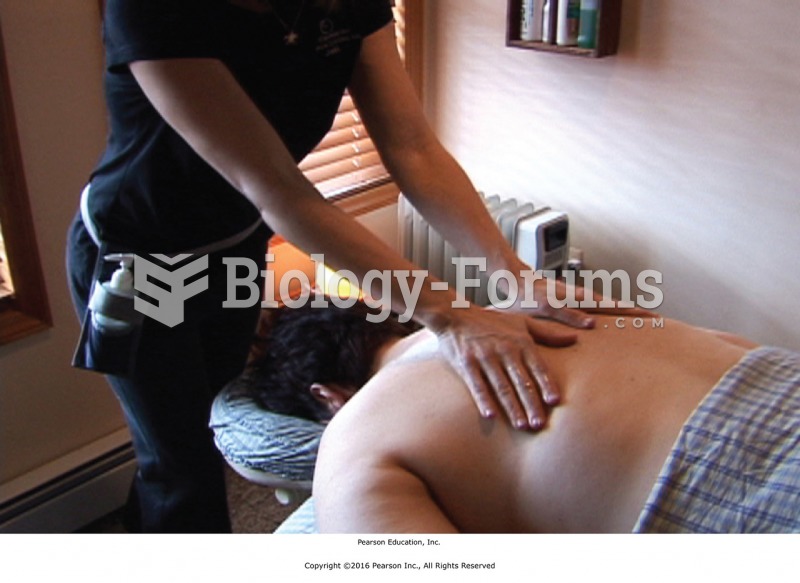 Good contact feels full, confident, and deliberate and establishes a warm connection between massage ...
Good contact feels full, confident, and deliberate and establishes a warm connection between massage ...
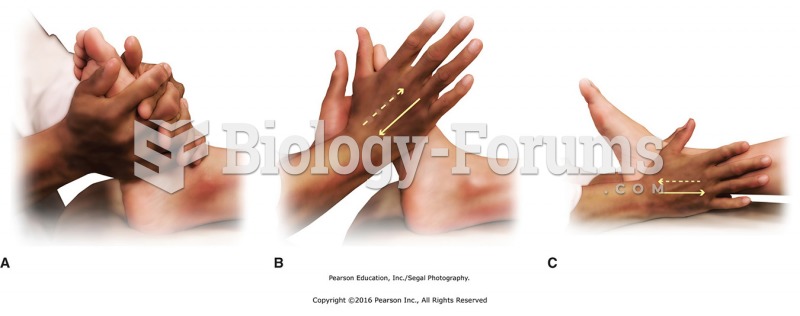 Warm-up (5 minutes). Warm up the soft tissues of the feet with a variety of kneading, sliding, and ...
Warm-up (5 minutes). Warm up the soft tissues of the feet with a variety of kneading, sliding, and ...