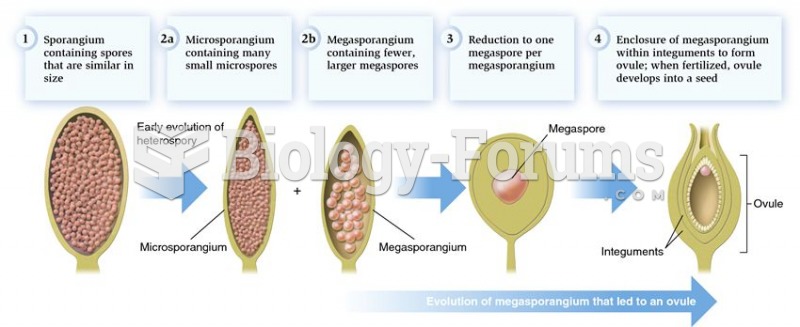
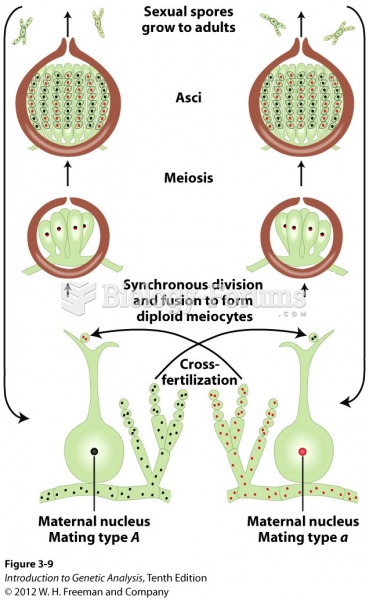
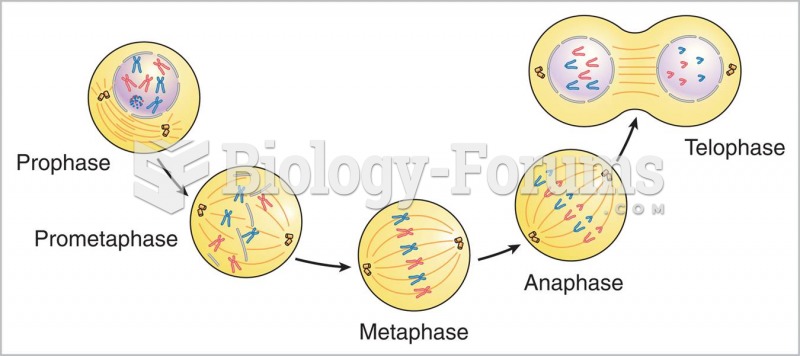
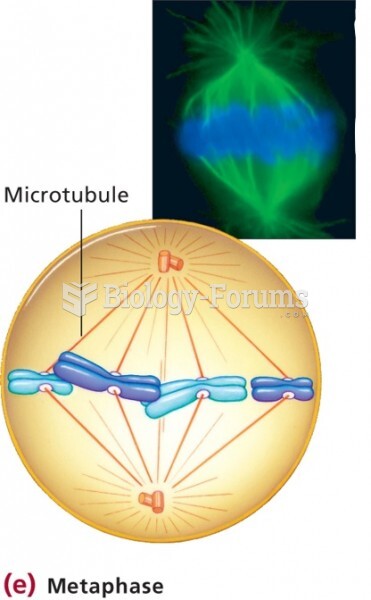
|
|
|
Children of people with alcoholism are more inclined to drink alcohol or use hard drugs. In fact, they are 400 times more likely to use hard drugs than those who do not have a family history of alcohol addiction.
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
Approximately 500,000 babies are born each year in the United States to teenage mothers.
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.