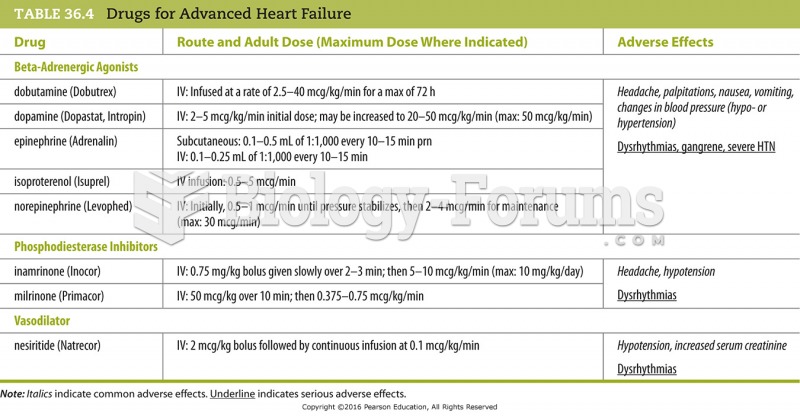
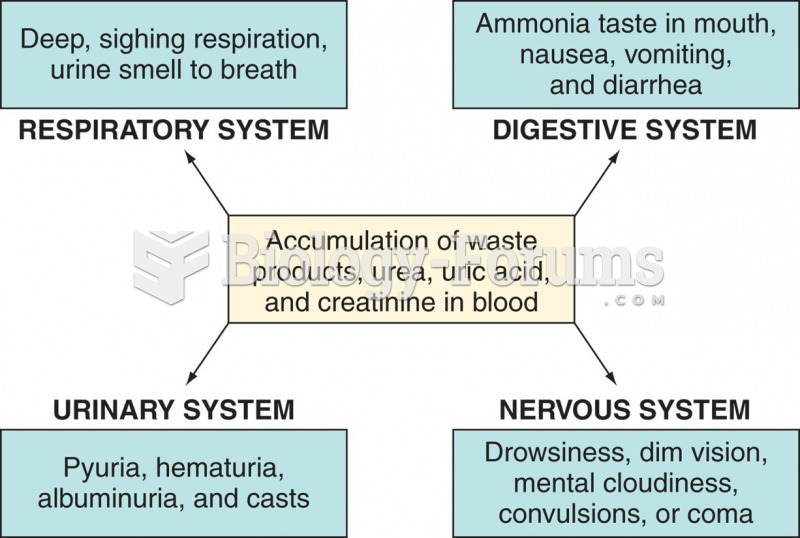
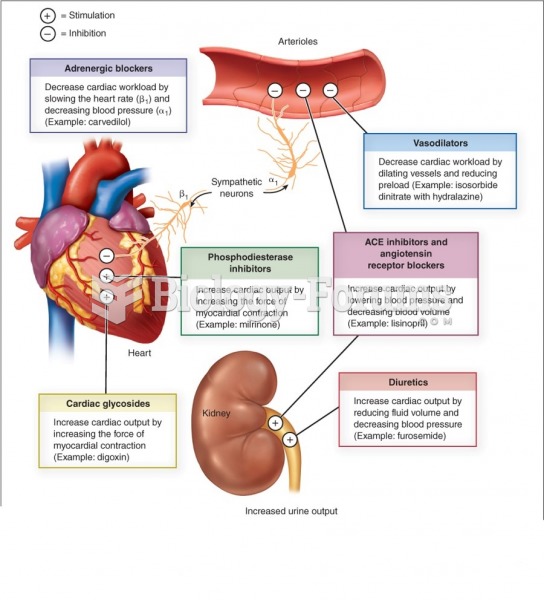
|
|
|
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.