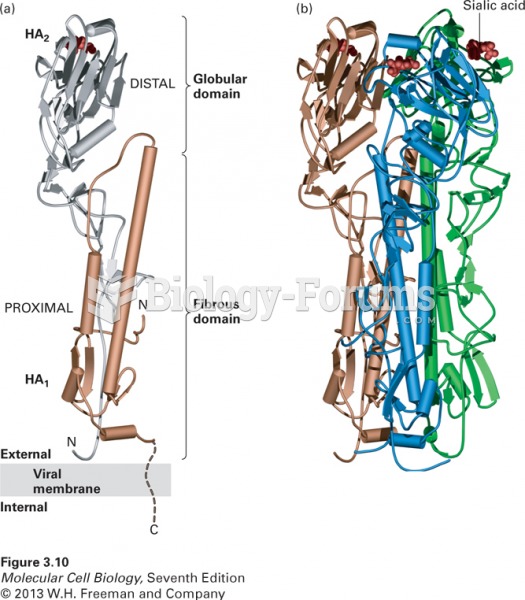
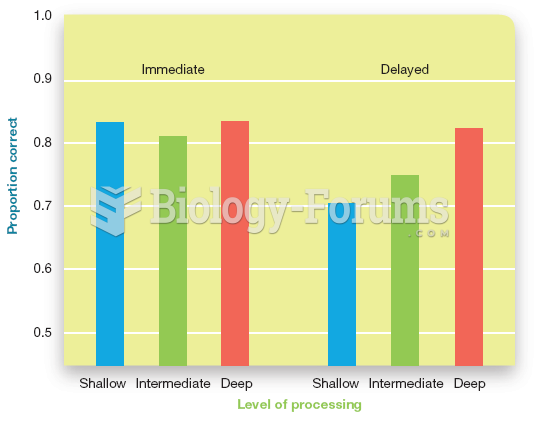
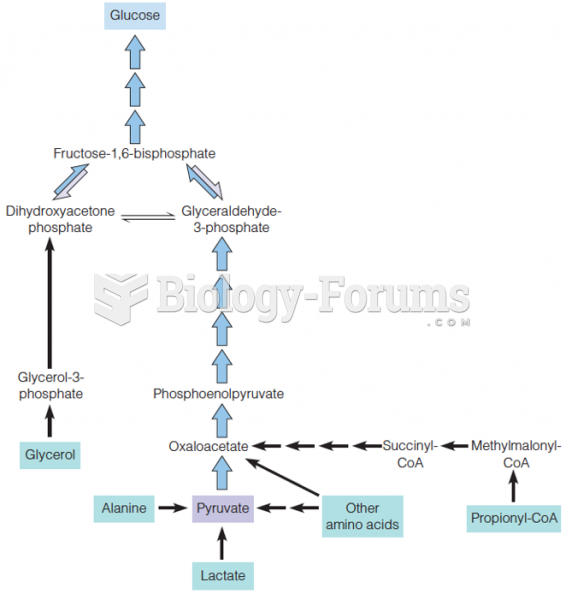
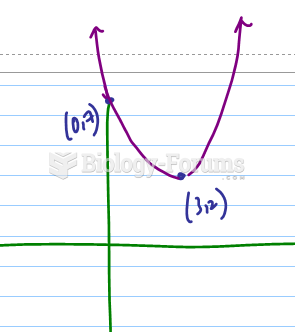
|
|
|
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Opium has influenced much of the world's most popular literature. The following authors were all opium users, of varying degrees: Lewis Carroll, Charles, Dickens, Arthur Conan Doyle, and Oscar Wilde.
Parkinson's disease is both chronic and progressive. This means that it persists over a long period of time and that its symptoms grow worse over time.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
All patients with hyperparathyroidism will develop osteoporosis. The parathyroid glands maintain blood calcium within the normal range. All patients with this disease will continue to lose calcium from their bones every day, and there is no way to prevent the development of osteoporosis as a result.