Answer to Question 1
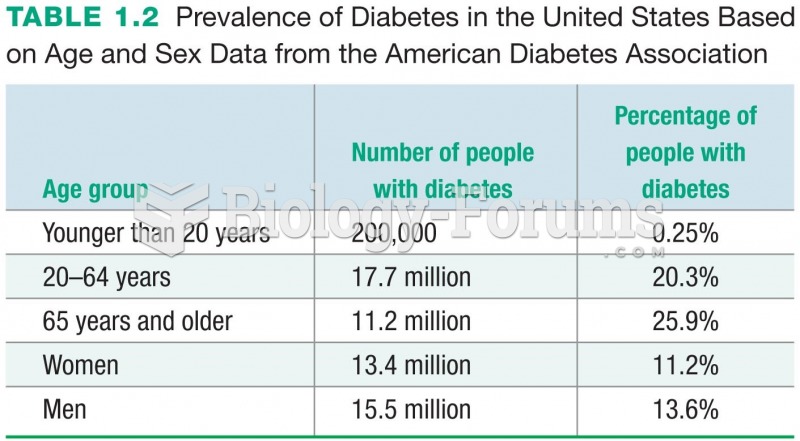
Folic acid deficiency is implicated in neural tube defects such as spina bifida, anencephaly, and encephalocele. Diabetes mellitus in the mother is also a risk factor for neural tube defects in the developing fetus.
Maternal serum marker testing measures AFP in the maternal blood. AFP is produced by the fetus and circulates freely when fetal membranes and blood vessels are exposed. It is therefore elevated with neural tube and ventral wall defects. Ultrasound is another useful test because it is able to visually detect fetal cranial and spinal defects in utero.
Teratogens produce their most detrimental effects on the fetus during the period of organogenesis. The most rapid time of organ development occurs from day 15 to day 60 after conception
Answer to Question 2
The three stages of carcinogenesis are as follows:
Initiation: this describes the exposure to a carcinogen. The exposure results in irreversible damage to the genome of an otherwise healthy cell. Such an exposure may be a one-time event, or it may occur in divided doses over a period of time.
Promotion: promotion may start soon after initiation or be delayed in a latent period. Promotion involves unregulated cell growth promoted by a variety of chemicals and growth factors.
Progression: this stage defines the malignant changes that occur in cells. These changes provide cancerous cells with the characteristic properties of invasiveness, metastatic competence, autonomous growth ability, and greater karyotype instability.
Fat and muscle wasting are a result of cancer anorexia-cachexia. The syndrome involves hypermetabolism and the altered processing of nutrients. Tumors consume glucose and produce lactate. Hypermetabolism occurs when, in an inefficient process, the liver uses the lactate for gluconeogenesis. The uncoupling of the oxidative phosphorylation process at the cellular level yields heat energy, contributing to poor energy utilization and hypermetabolism. Finally, instead of sparing amino acids when generating energy, muscle mass is depleted together with fat stores. Muscle wasting, weakness, and weight loss are the result.
Lambert-Eaton syndrome is a paraneoplastic neurologic disorder seen in some patients with small cell lung cancer. The cancer cells produce onconeural antigens that trigger an immune reaction. If antibodies and primed lymphocytes are able to cross the blood-brain barrier, they recognize the neurons associated with the antigen and mount an immune response against the cells.