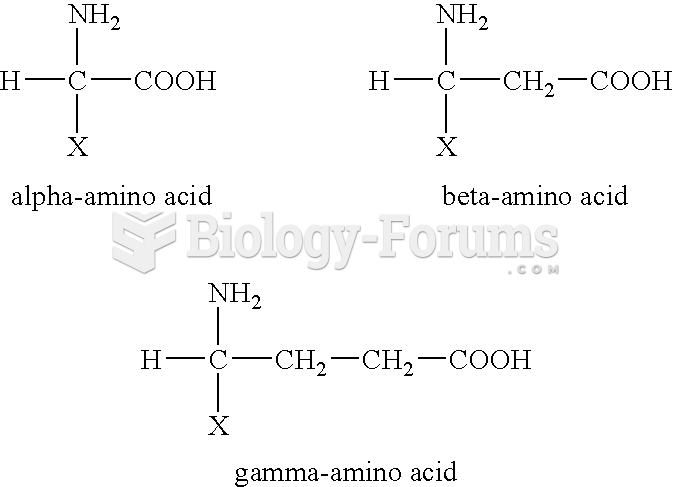
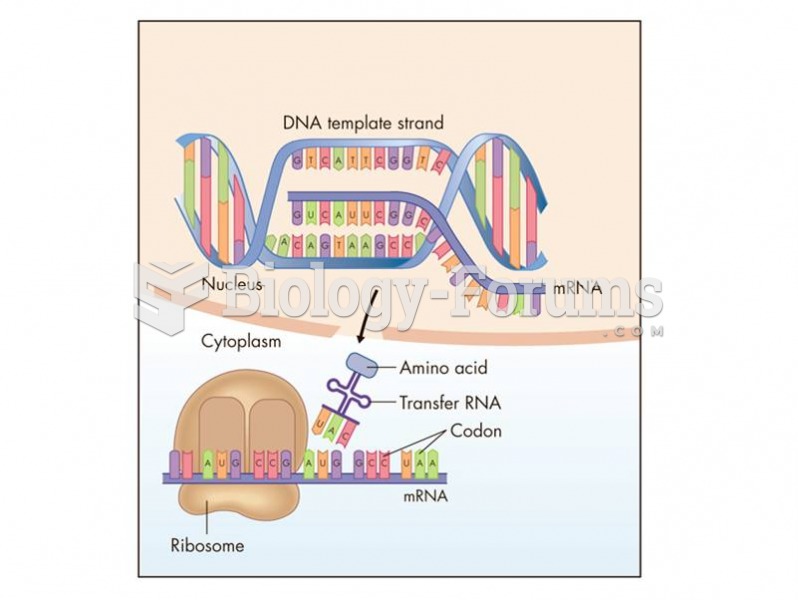
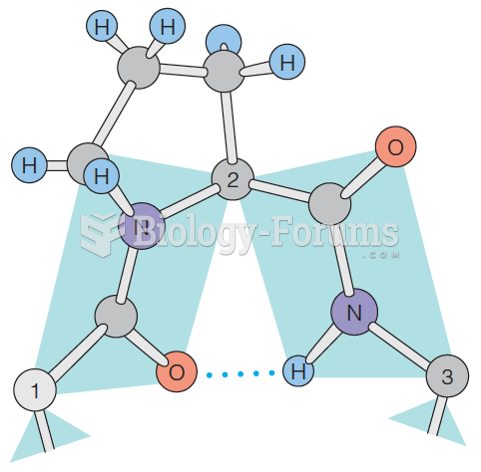
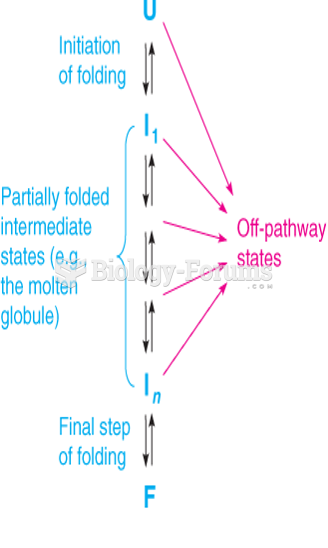
|
|
|
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
Barbituric acid, the base material of barbiturates, was first synthesized in 1863 by Adolph von Bayer. His company later went on to synthesize aspirin for the first time, and Bayer aspirin is still a popular brand today.
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.