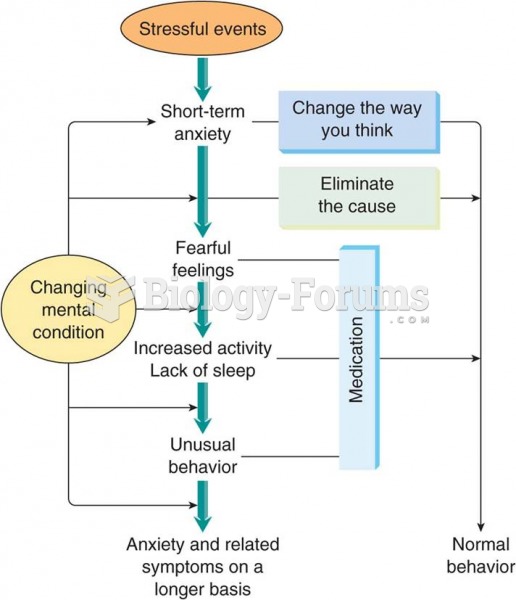
Answer to Question 1
Benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam, should be used only on a short-term basis when a quick-
acting medication is needed until another medication, such as an antidepressant, takes effect. The
benzodiazepine may be slowly tapered, depending on the length of therapy, and discontinued.
Anxiolytics:Alprazolam (Xanax), lorazepam (Ativan), and clonazepam (Klonopin) are used for short-
term treatment of panic disorder. They are taken on an as-needed (PRN) basis because of the
potential for addiction. They should not be taken with other central nervous system medications
because of potential for overdose and respiratory arrest. The patient should not drive after taking
these medications. Side effects might include drowsiness, poor coordination, and dry mouth.
Nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytics:Buspirone (BuSpar) has no potential for addiction. However, some
practitioners do not consider this drug to be as effective as others for panic disorder. It takes
2 to 4 weeks for buspirone to reach full effectiveness. Common side effects include dizziness,
headache, drowsiness, and nausea. It should not be taken with grapefruit or related citrus fruits.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs):These agents include fluoxetine (Prozac), paroxetine
(Paxil), sertraline (Zoloft), and venlafaxine (Effexor). Patients should take these medications as
prescribed. Symptoms might not improve for 2 to 4 weeks. Side effects may include sweating,
sedation, agitation, gastrointestinal upset (if taken without food), decreased libido, and
lightheadedness. The dosage can be adjusted periodically to ensure medication efficacy. These
medications must not be stopped abruptly.
Answer to Question 2
Physiologic disorders
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Life transitions (e.g., moving, job change, divorce, retirement)
Grief reactions
Terminal illness
Anticipation of upcoming events
Present abuse situation
Loss of security
Homelessness
Substance abuse
Panic attacks begin with intense fear or discomfort; symptoms develop abruptly and reach a peak
within about 10 minutes. The two types are unexpected and expected panic attacks.
Panic disorder is the presence of recurrent, unexpected panic attacks followed by at least 1 month
of persistent concern about having another panic attack, worry about the consequences of panic
attacks, or significant behavioral change related to the attacks.
G.G. had an unexpected panic attack. This type occurs suddenly and without warning that the attack
is about to occur. Expected panic attacks occur in response to a specific fear. For example, a person
with a fear of heights has a panic attack when on an airplane or in an upper story of a tall building.
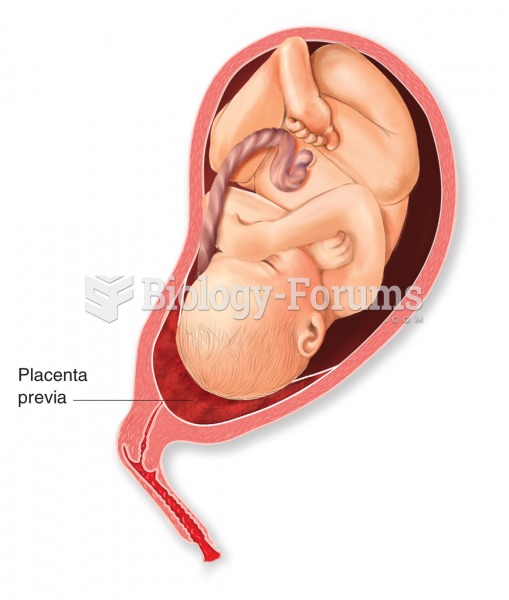 Placenta previa. The condition is caused by the development of the placenta over the cervical canal,
Placenta previa. The condition is caused by the development of the placenta over the cervical canal,
 A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern
A client is having an endoscopy performed by a physician who views the upper gastrointestinal intern