|
|
|
Hippocrates noted that blood separates into four differently colored liquids when removed from the body and examined: a pure red liquid mixed with white liquid material with a yellow-colored froth at the top and a black substance that settles underneath; he named these the four humors (for blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile).
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.
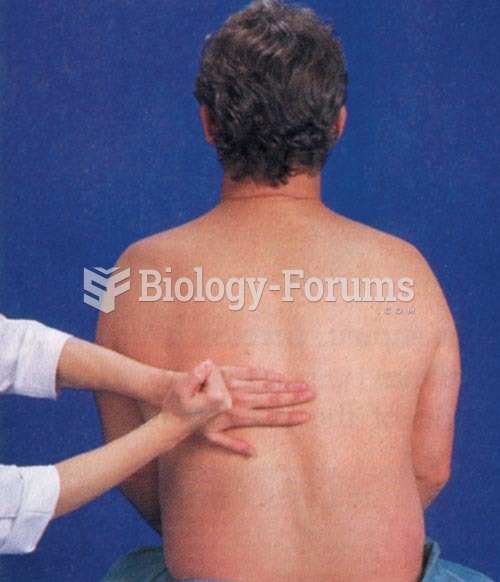
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
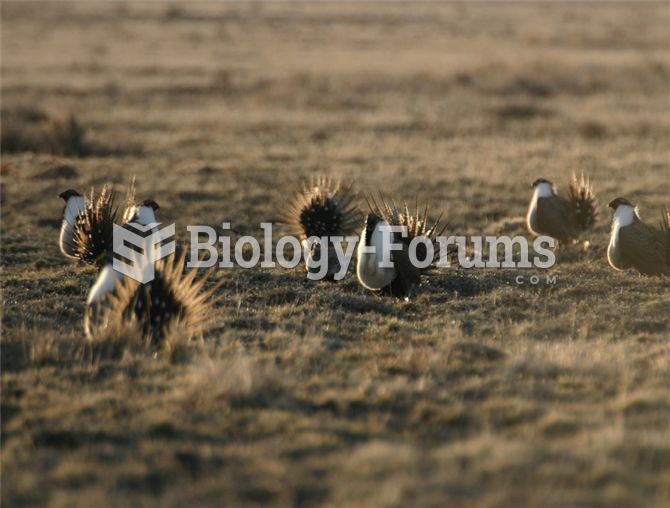 Organisms exhibit a diversity of behaviours, which include (clockwise from upper left), foraging and
Organisms exhibit a diversity of behaviours, which include (clockwise from upper left), foraging and
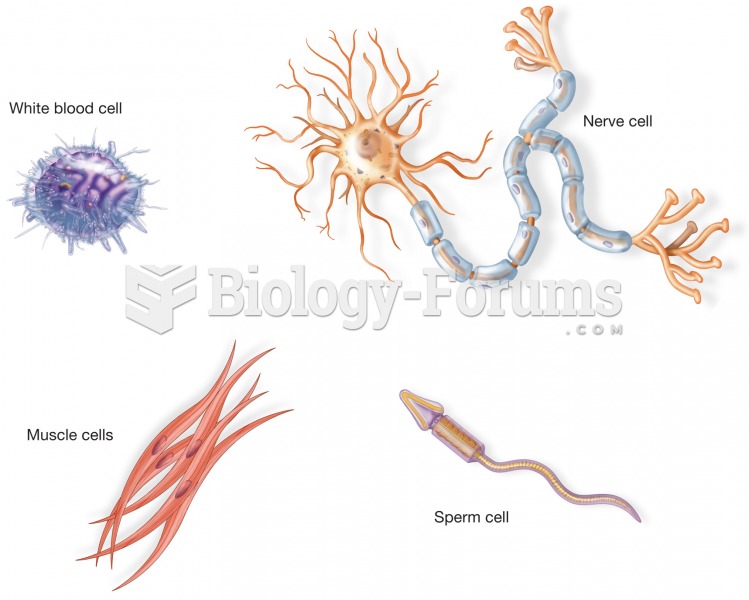 Examples of four different types of cells from the body. Although each cell has a cell membrane, nuc
Examples of four different types of cells from the body. Although each cell has a cell membrane, nuc