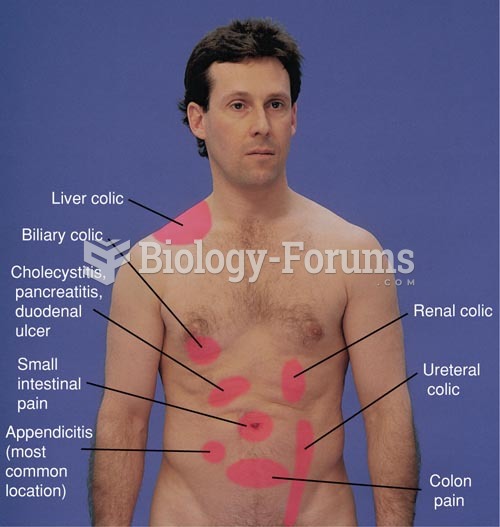
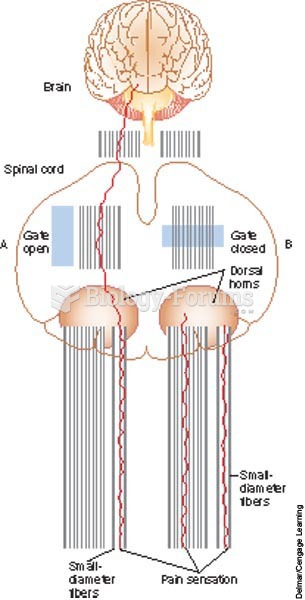
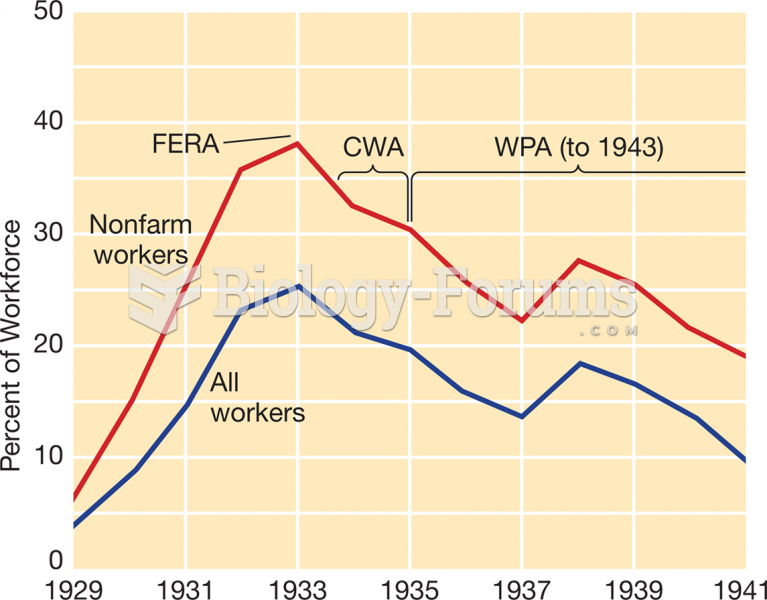
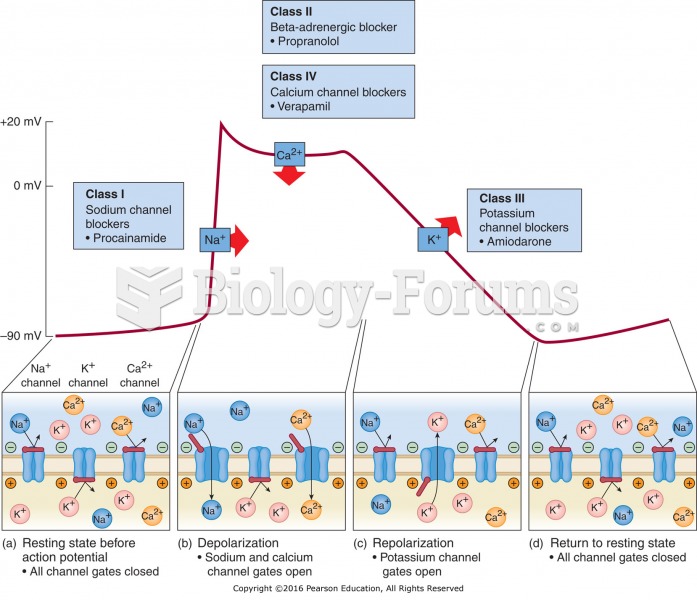
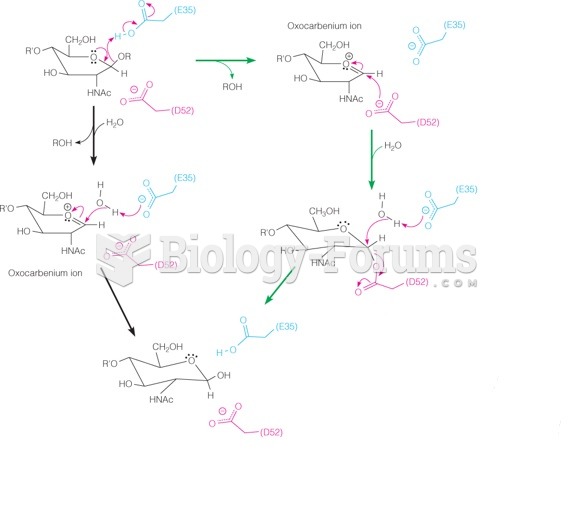
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.
Did you know?
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Did you know?
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
Did you know?
Approximately 500,000 babies are born each year in the United States to teenage mothers.
Did you know?
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.