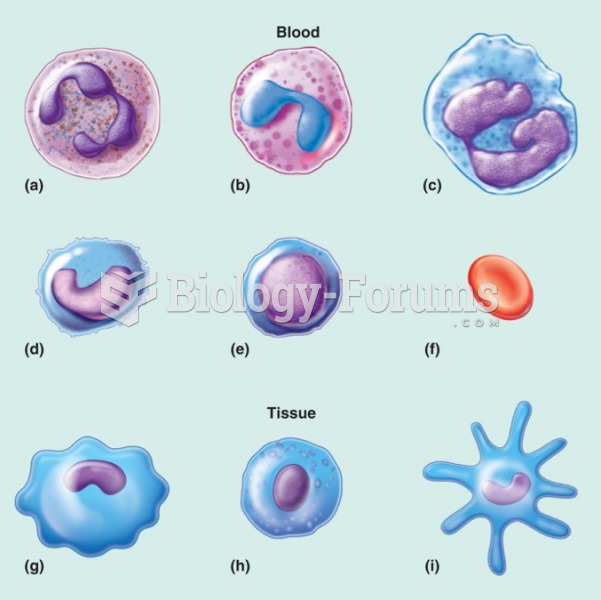
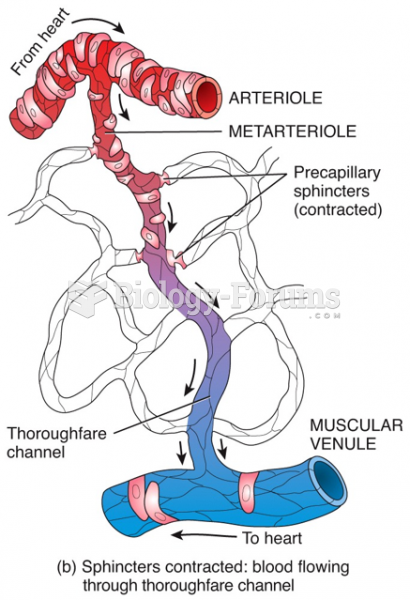
|
|
|
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
There used to be a metric calendar, as well as metric clocks. The metric calendar, or "French Republican Calendar" divided the year into 12 months, but each month was divided into three 10-day weeks. Each day had 10 decimal hours. Each hour had 100 decimal minutes. Due to lack of popularity, the metric clocks and calendars were ended in 1795, three years after they had been first marketed.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
Children of people with alcoholism are more inclined to drink alcohol or use hard drugs. In fact, they are 400 times more likely to use hard drugs than those who do not have a family history of alcohol addiction.