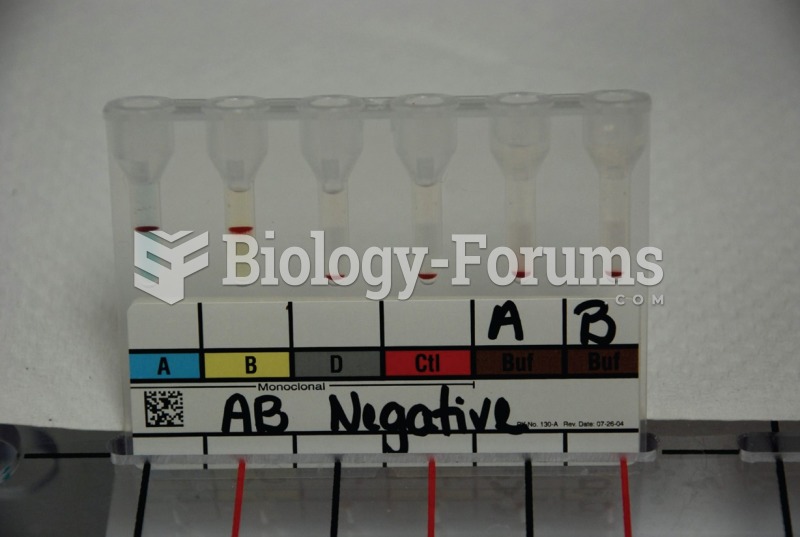
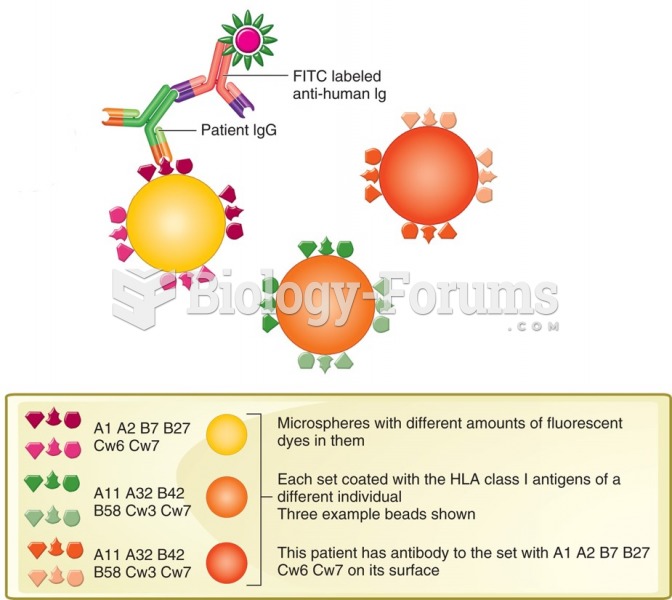
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are more nerve cells in one human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way.
Did you know?
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Did you know?
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.
Did you know?
Though the United States has largely rejected the metric system, it is used for currency, as in 100 pennies = 1 dollar. Previously, the British currency system was used, with measurements such as 12 pence to the shilling, and 20 shillings to the pound.
Did you know?
Stroke kills people from all ethnic backgrounds, but the people at highest risk for fatal strokes are: black men, black women, Asian men, white men, and white women.