|
|
|
Did you know?
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
Did you know?
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Did you know?
To maintain good kidney function, you should drink at least 3 quarts of water daily. Water dilutes urine and helps prevent concentrations of salts and minerals that can lead to kidney stone formation. Chronic dehydration is a major contributor to the development of kidney stones.
Did you know?
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.
Did you know?
Eat fiber! A diet high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by as much as 10%.
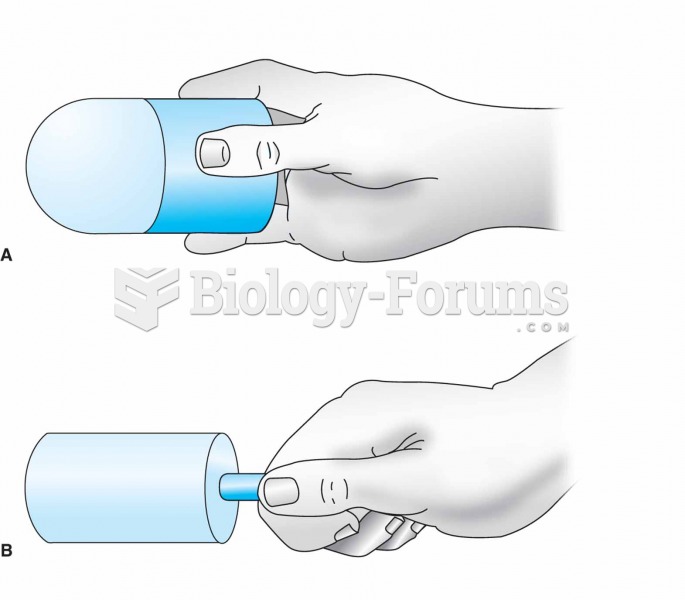 For ice massage, ice is frozen in a cylindrical container or a paper cup (A). The top half of the cu
For ice massage, ice is frozen in a cylindrical container or a paper cup (A). The top half of the cu
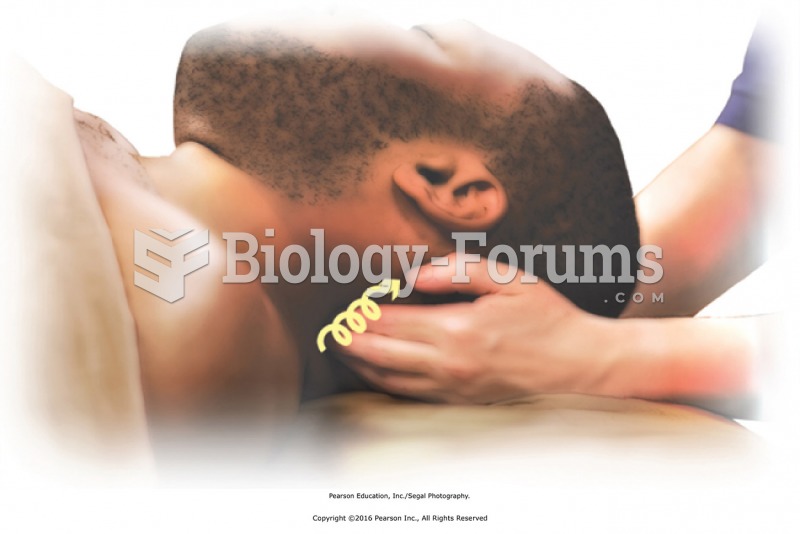 Apply circular friction to the left side of the neck along cervical muscles with the fingertips of ...
Apply circular friction to the left side of the neck along cervical muscles with the fingertips of ...
 A boiling-liquid, expanding-vapor explosion (BLEVE). The burning propane cylinder on the left is not ...
A boiling-liquid, expanding-vapor explosion (BLEVE). The burning propane cylinder on the left is not ...