|
|
|
Sildenafil (Viagra®) has two actions that may be of consequence in patients with heart disease. It can lower the blood pressure, and it can interact with nitrates. It should never be used in patients who are taking nitrates.
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
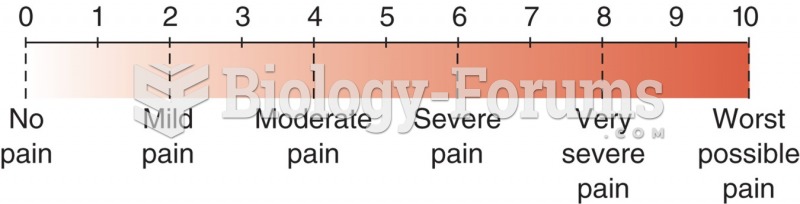
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.