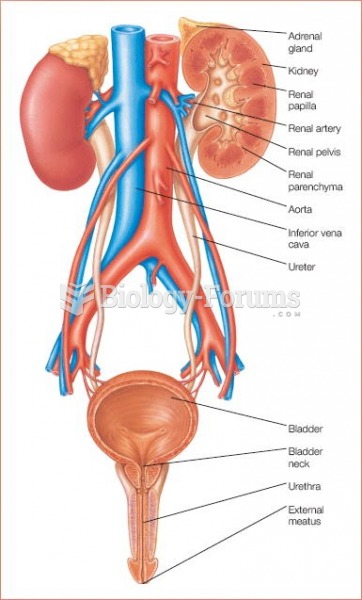
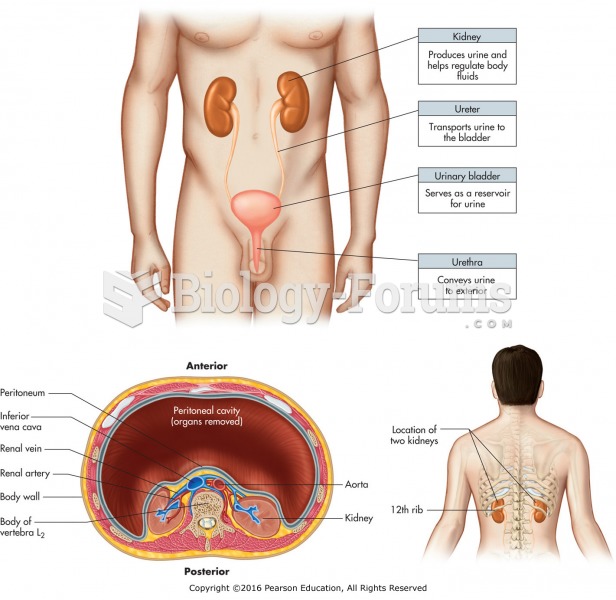
|
|
|
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.