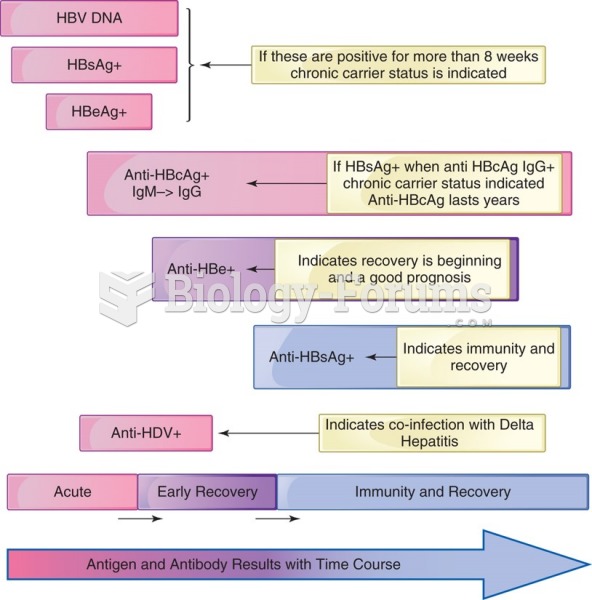
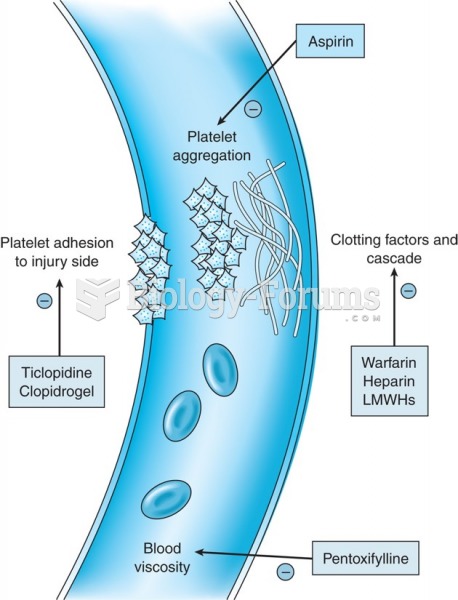
|
|
|
Did you know?
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
Did you know?
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Did you know?
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
Did you know?
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
Did you know?
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.