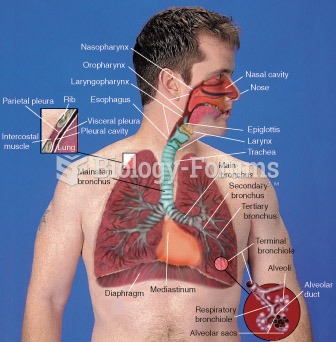
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Did you know?
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Did you know?
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
Did you know?
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").
Did you know?
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.