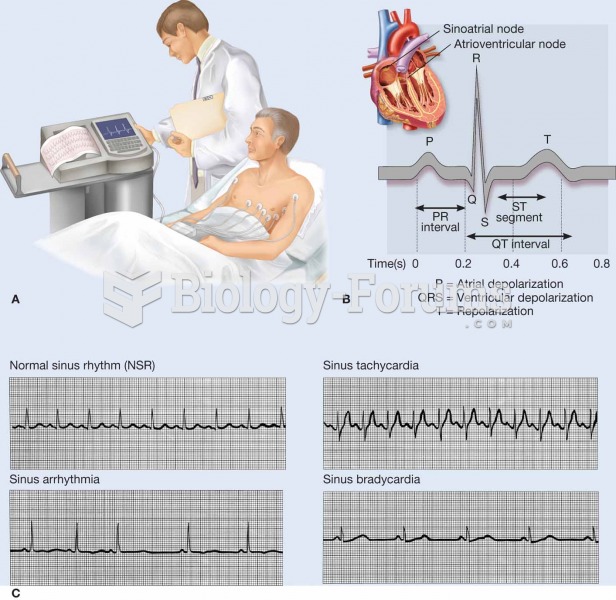
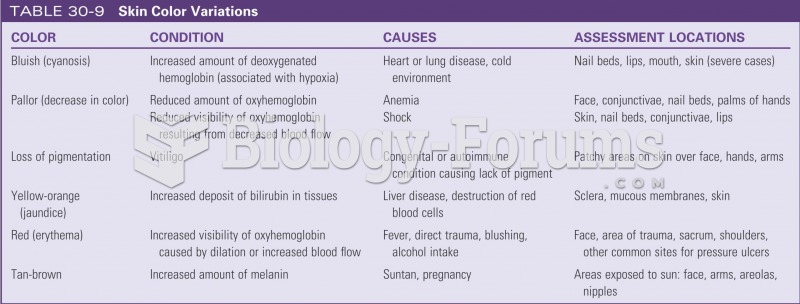
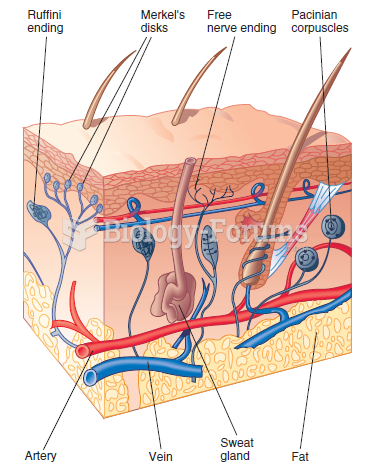
|
|
|
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
Oliver Wendell Holmes is credited with introducing the words "anesthesia" and "anesthetic" into the English language in 1846.
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.