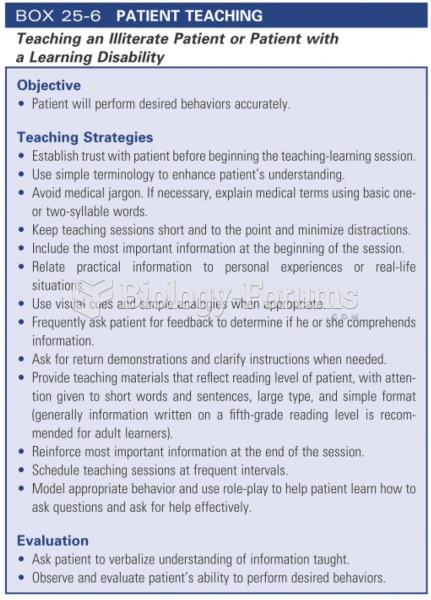
|
|
|
Disorders that may affect pharmacodynamics include genetic mutations, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's disease, and certain forms of insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus.
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).
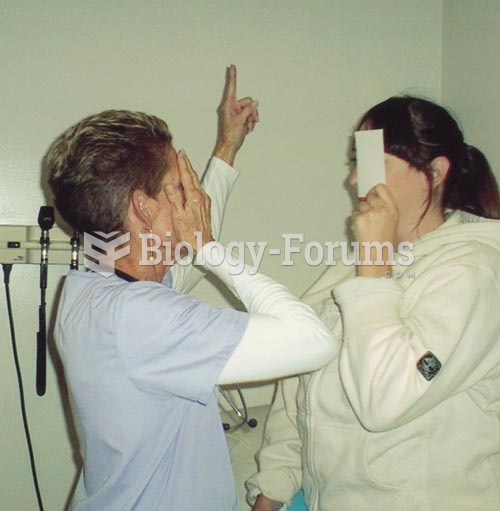 Testing Visual Fields by Confrontation: The nurse and patient should be approximately at an eye to e
Testing Visual Fields by Confrontation: The nurse and patient should be approximately at an eye to e
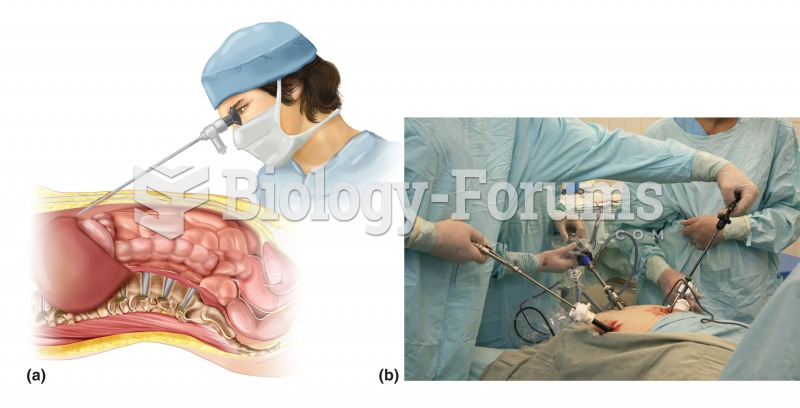 GI endoscopy. (a) Similar to other forms of GI endoscopy, laparoscopy involves the insertion of a sp
GI endoscopy. (a) Similar to other forms of GI endoscopy, laparoscopy involves the insertion of a sp