|
|
|
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
All adults should have their cholesterol levels checked once every 5 years. During 2009–2010, 69.4% of Americans age 20 and older reported having their cholesterol checked within the last five years.
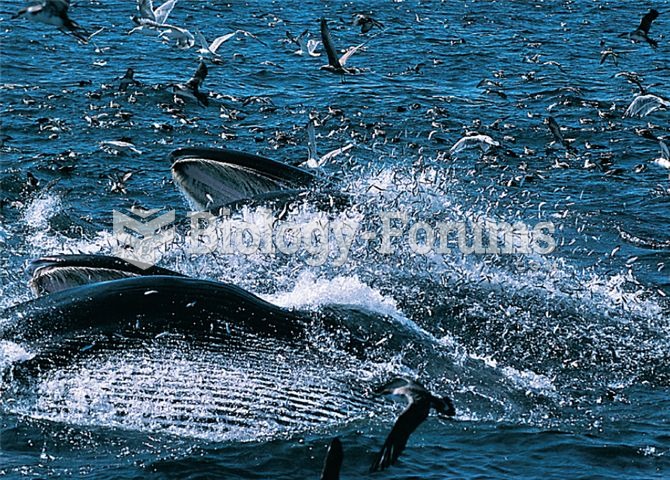
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.