|
|
|
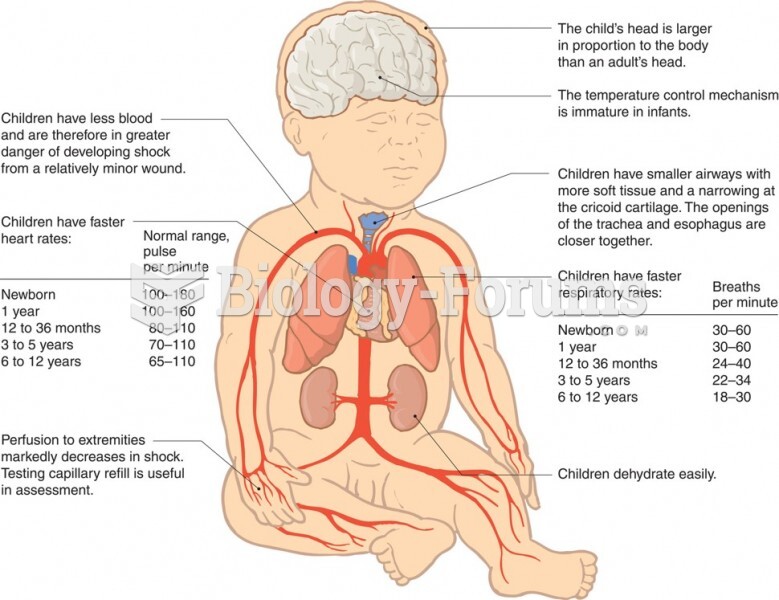
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
Tobacco depletes the body of vitamins A, C, and E, which can result in any of the following: dry hair, dry skin, dry eyes, poor growth, night blindness, abscesses, insomnia, fatigue, reproductive system problems, sinusitis, pneumonia, frequent respiratory problems, skin disorders, weight loss, rickets, osteomalacia, nervousness, muscle spasms, leg cramps, extremity numbness, bone malformations, decayed teeth, difficulty in walking, irritability, restlessness, profuse sweating, increased uric acid (gout), joint damage, damaged red blood cells, destruction of nerves, infertility, miscarriage, and many types of cancer.
 The nurse needs to inform the patient with impaired vision when a touch is to occur and ask permissi
The nurse needs to inform the patient with impaired vision when a touch is to occur and ask permissi
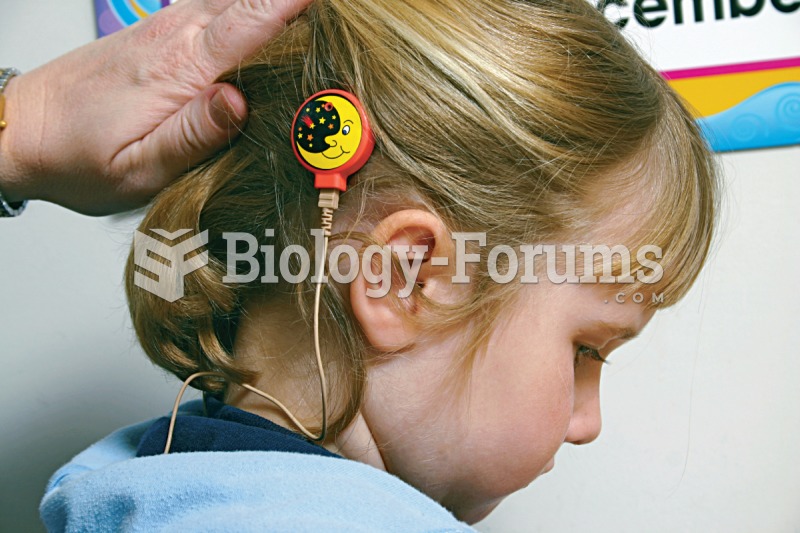 Photograph of a child with a cochlear implant. This device sends electrical impulses directly to the
Photograph of a child with a cochlear implant. This device sends electrical impulses directly to the
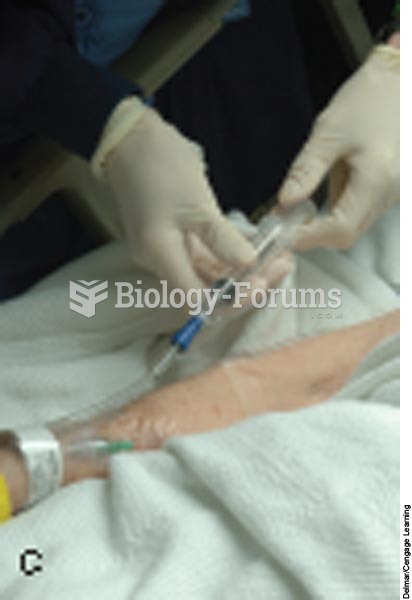 Injecting an IV push (bolus) medication; C, another type of needleless syringe and needleless IV acc
Injecting an IV push (bolus) medication; C, another type of needleless syringe and needleless IV acc