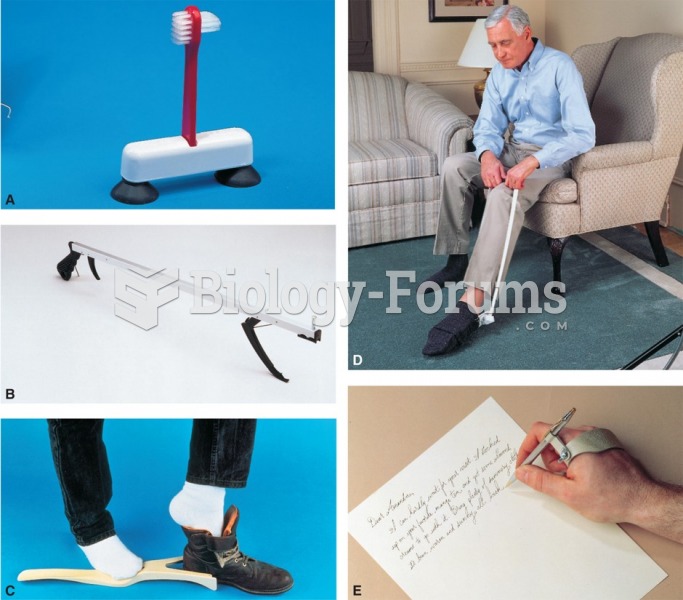
Answer to Question 1
Formal marketing controls are overt in their attempt to influence employee behavior and marketing performance. Informal controls, on the other hand, are more subtle. Informal marketing controls are unwritten, employee-based mechanisms that subtly affect the behaviors of employees, both as individuals and in groups. Here, we deal with personal objectives and behaviors as well as group-based norms and expectations. There are three types of informal control: employee self-control, social control, and cultural control.
Employee Self-Control-Through employee self-control, employees manage their own behaviors (and thus the implementation of the marketing strategy) by establishing personal objectives and monitoring their results. The type of personal objectives that employees set depends on how they feel about their jobs. If they have high job satisfaction and a strong commitment to the firm, they are more likely to establish personal objectives that are consistent with the aims of the firm, the marketing strategy, and the firm's goals and objectives. Employee self-control also depends on the rewards that employees receive. Some employees prefer the intrinsic rewards of doing a good job rather than the extrinsic rewards of pay and recognition. Intrinsically rewarded employees are likely to exhibit more self-control by managing their behaviors in ways consistent with the marketing strategy.
Social Control-Social, or small group, control deals with the standards, norms, and ethics found in work groups within the firm. The social interaction that occurs within these work groups can be a powerful motivator of employee behavior. The social and behavioral norms of work groups provide the peer pressure that causes employees to conform to expected standards of performance. If employees fall short of these standards, the group will pressure them to align with group norms. This pressure can be both positive and negative. Positive group influence can encourage employees to increase their effort and performance in ways consistent with the firm's goals and objectives. However, the opposite is also true. If the work group's norms encourage slacking or shirking of job responsibilities, employees will feel pressured to conform or risk being ostracized for good work.
Cultural Control-Cultural control is very similar to social control, only on a much broader scale. Here, we concern ourselves with the behavioral and social norms of the entire firm. One of the most important outcomes of cultural control is the establishment of shared values among all members of the firm. Marketing implementation is most effective and efficient when every employee, guided by the same organizational values or beliefs, has a commitment to the same organizational goals. Unfortunately, cultural control is very difficult to master, in that it takes a great deal of time to create the appropriate organizational culture to ensure implementation success.
Answer to Question 2
True