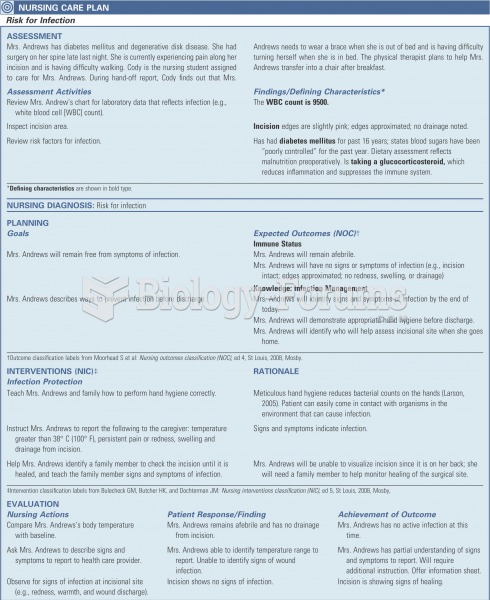
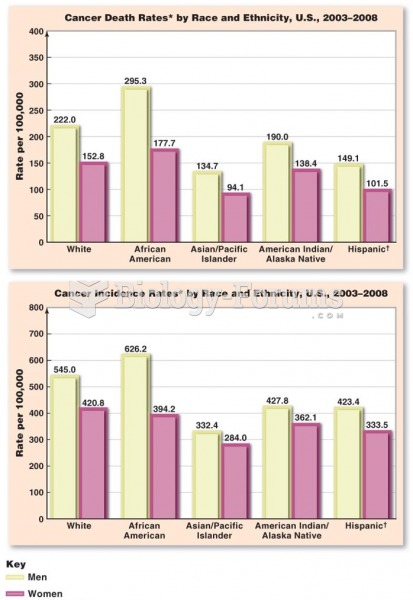
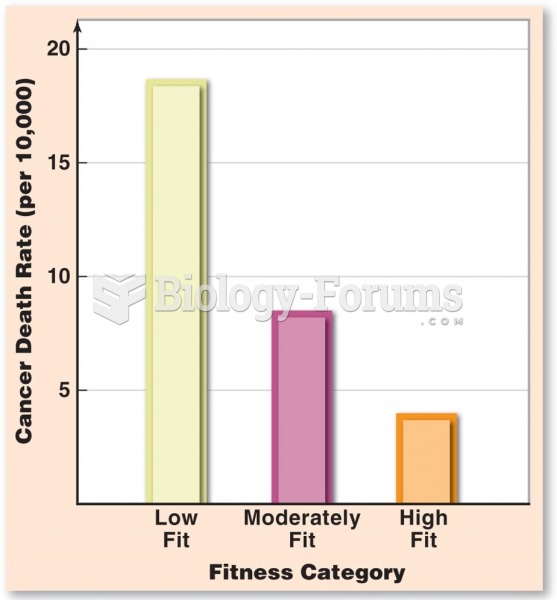
|
|
|
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
About 3% of all pregnant women will give birth to twins, which is an increase in rate of nearly 60% since the early 1980s.
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Hippocrates noted that blood separates into four differently colored liquids when removed from the body and examined: a pure red liquid mixed with white liquid material with a yellow-colored froth at the top and a black substance that settles underneath; he named these the four humors (for blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile).