|
|
|
In 1886, William Bates reported on the discovery of a substance produced by the adrenal gland that turned out to be epinephrine (adrenaline). In 1904, this drug was first artificially synthesized by Friedrich Stolz.
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Since 1988, the CDC has reported a 99% reduction in bacterial meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, due to the introduction of the vaccine against it.
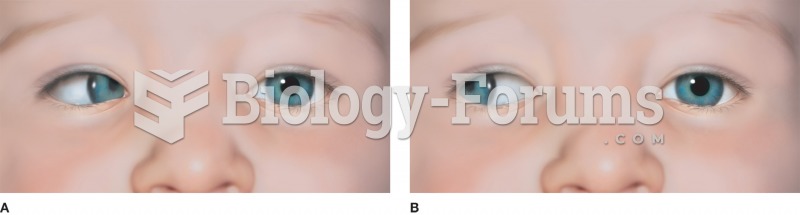 Examples of common forms of strabismus: (A) esotropia with the right eye turning inward and (B) exot
Examples of common forms of strabismus: (A) esotropia with the right eye turning inward and (B) exot
 French and U.S. presidential elections in 2012 illustrate the durability of political culture and ho
French and U.S. presidential elections in 2012 illustrate the durability of political culture and ho