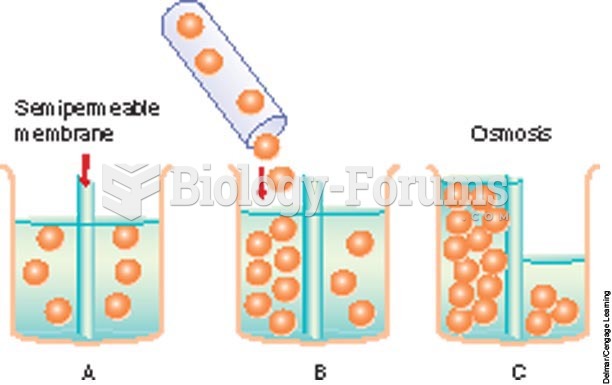
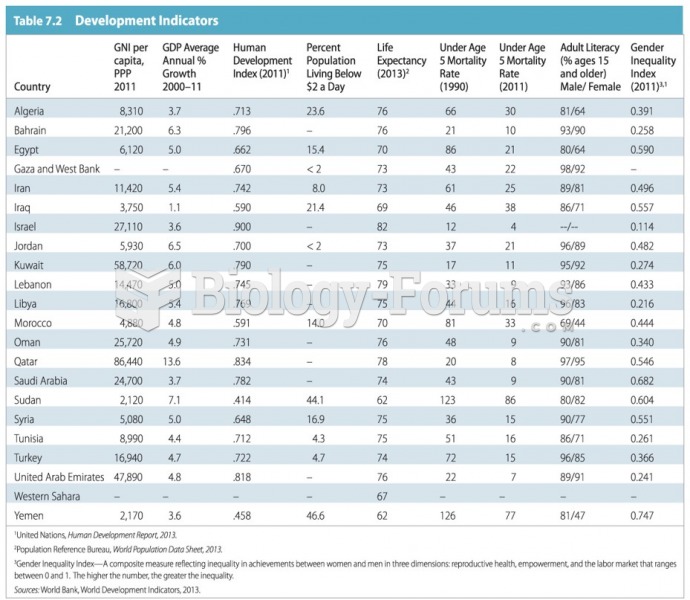
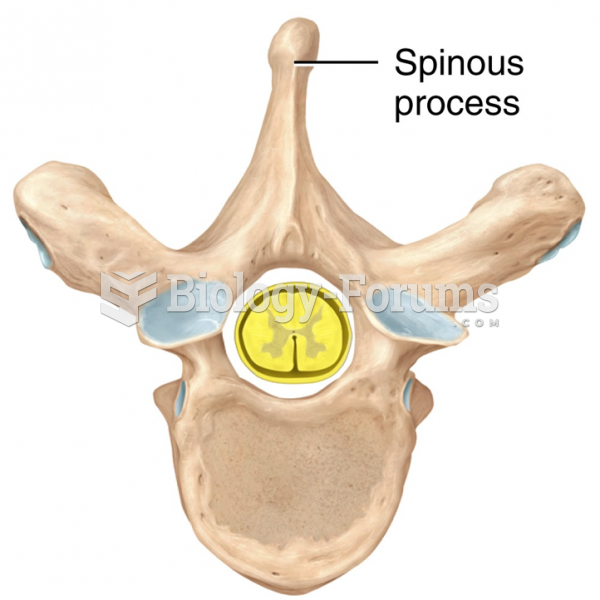
Answer to Question 1
During the 20th century, life expectancy steadily increased as industrialized nations developed better water and sewage systems, improved nutrition, and made tremendous advances in medical science. However, children today are often viewed as an economic liability they cannot contribute to the family's financial well-being and must be supported. Consequently, children are expected to attend school and learn the necessary skills for future employment rather than perform unskilled labor. Further, older people are typically expected to retire so that younger people can assume their economic, political, and social roles. In the United States, age differentiation is typically based on categories such as infancy, childhood, adolescence, young adulthood, middle adulthood, and later adulthood. Age stratification is the inequalities, differences, segregation, or conflict between age groups. Infancy (birth to age 2) and childhood (ages 3 to 12) are typically thought of as carefree years, however, children are among the most powerless and vulnerable people in society. Historically, children were seen as the property of their parents, who could do with them as they pleased. Early socialization plays a significant part in children's experiences and their quality of life.
Many children are confronted with an array of problems in their families because of marital instability, an increase in the number of single-parent households, and the percentage of families in which both parents are employed full time. These factors have heightened the need for high-quality, affordable child care for infants and young children. In contemporary industrialized countries, adolescence roughly spans the teenage years (ages 13 to 19).
Today, young people are expected to continue their education and perhaps hold a part-time job. Adolescents are not granted full status as adults in most societies, but they are more responsible than younger children. Many adolescents also face conflicting demands to attend school and to make money. Among the most pressing adolescent problems identified were crime and violence, teen pregnancy, suicide, drug abuse, and excessive peer pressure. The primary way to save the adolescent generation of today is to reduce poverty among children, teenagers, and young families.
Answer to Question 2
True