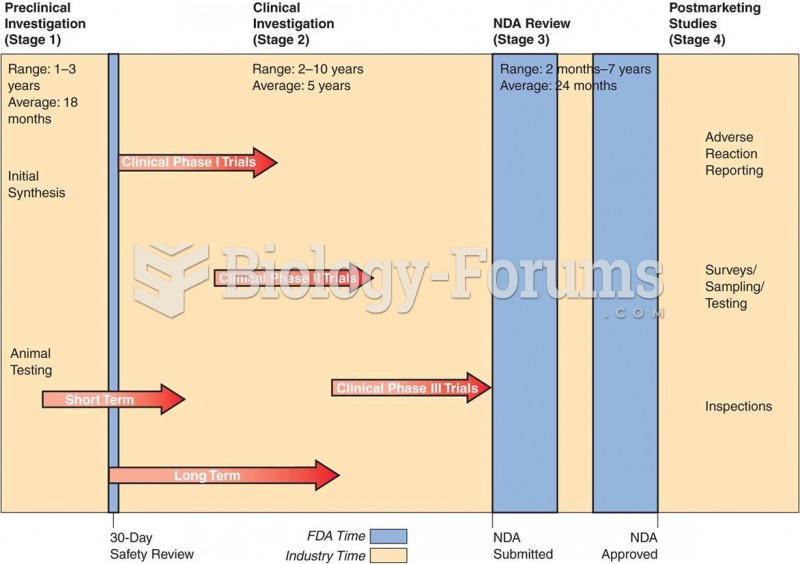
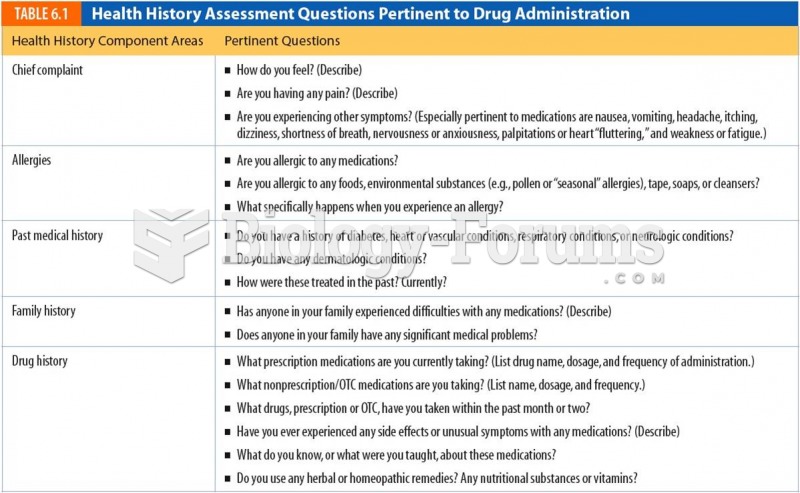
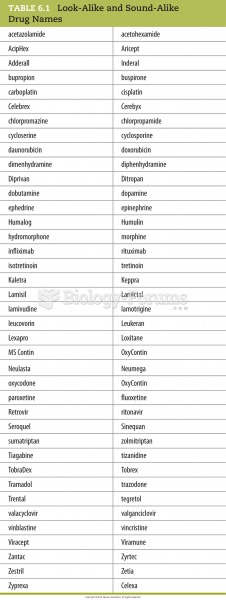
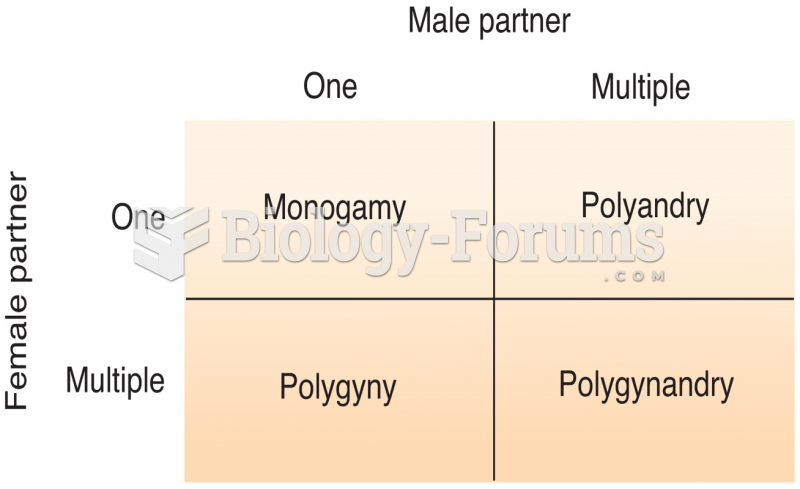
|
|
|
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.