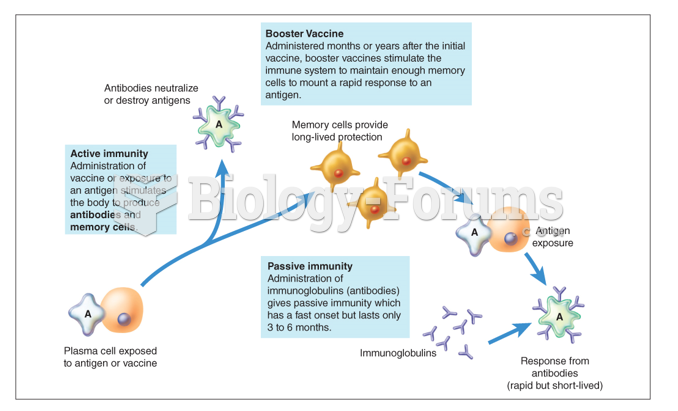
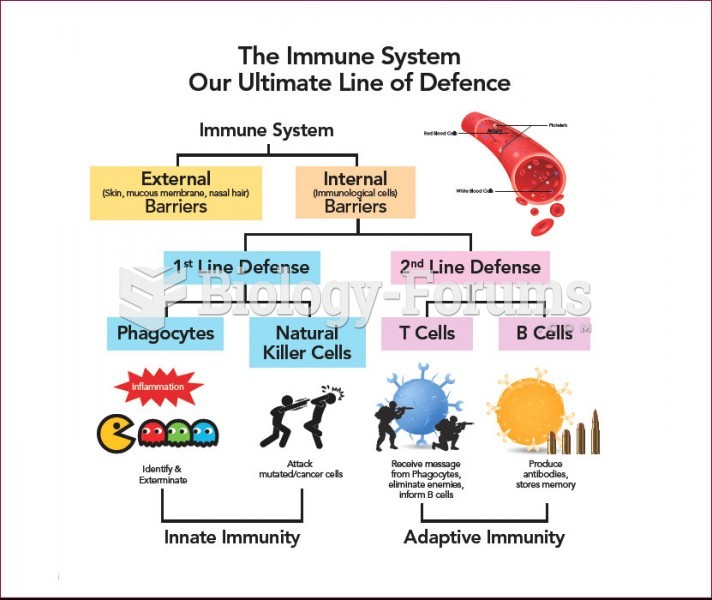
|
|
|
Women are two-thirds more likely than men to develop irritable bowel syndrome. This may be attributable to hormonal changes related to their menstrual cycles.
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
According to animal studies, the typical American diet is damaging to the liver and may result in allergies, low energy, digestive problems, and a lack of ability to detoxify harmful substances.
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
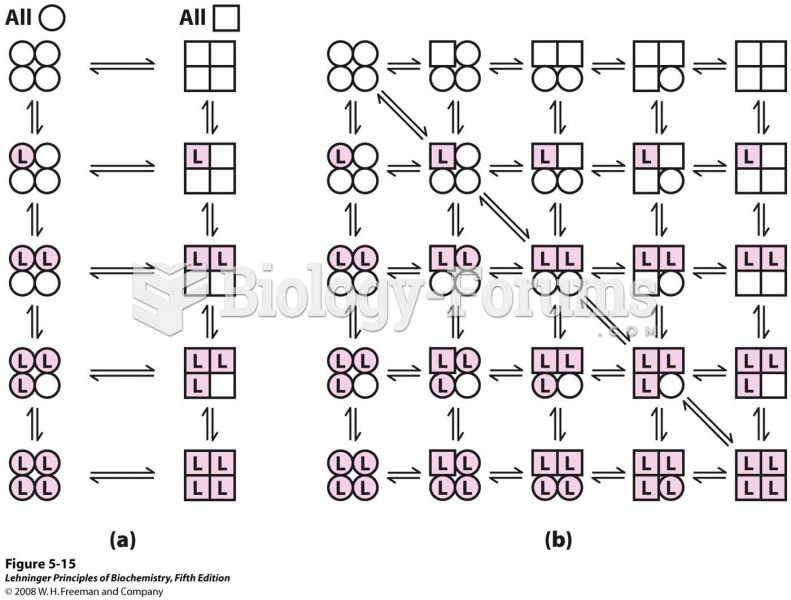 Two general models for the interconversion of inactive and active forms of a protein during cooperat
Two general models for the interconversion of inactive and active forms of a protein during cooperat
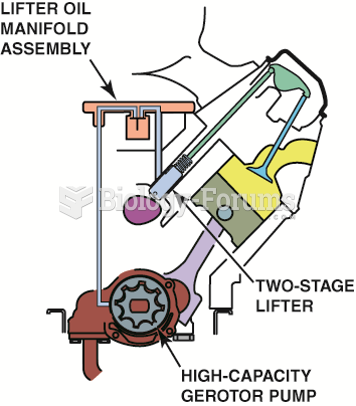 Active fuel management includes many different components and changes to the oiling system, which ...
Active fuel management includes many different components and changes to the oiling system, which ...
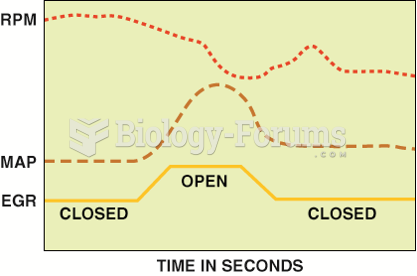 An OBD-II active test. The PCM opens the EGR valve and then monitors the MAP sensor and/or engine ...
An OBD-II active test. The PCM opens the EGR valve and then monitors the MAP sensor and/or engine ...