|
|
|
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.
When Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, he called "zero degrees" the lowest temperature he was able to attain with a mixture of ice and salt. For the upper point of his scale, he used 96°, which he measured as normal human body temperature (we know it to be 98.6° today because of more accurate thermometers).
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
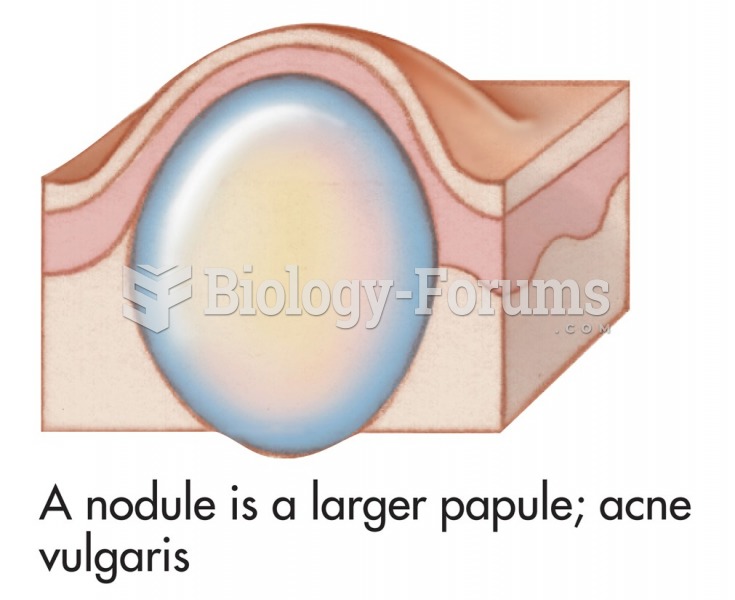 Common skin signs are often evidence of an illness or disorder. A nodule is a larger papule; acne ...
Common skin signs are often evidence of an illness or disorder. A nodule is a larger papule; acne ...
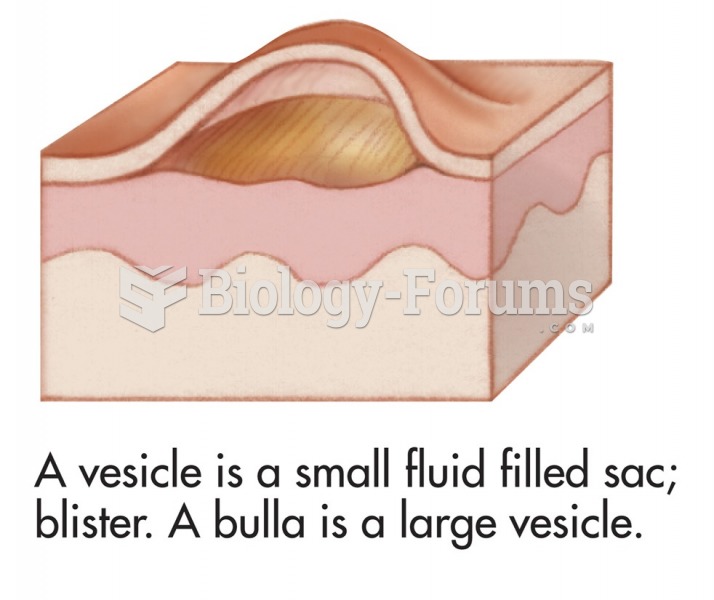 Common skin signs are often evidence of an illness or disorder. A vesicle is a small fluid filled ...
Common skin signs are often evidence of an illness or disorder. A vesicle is a small fluid filled ...