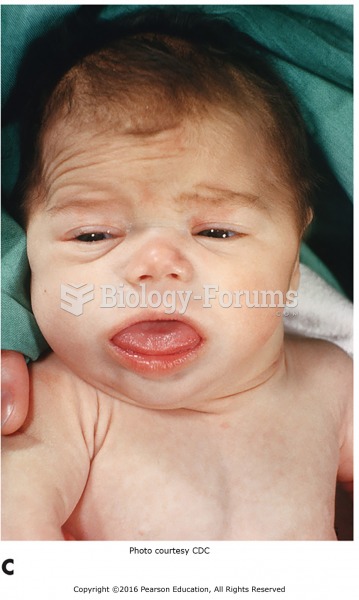
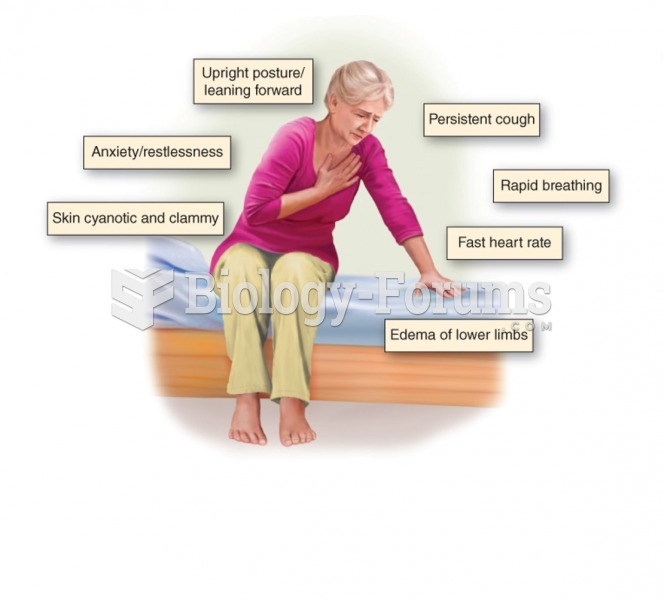
|
|
|
To maintain good kidney function, you should drink at least 3 quarts of water daily. Water dilutes urine and helps prevent concentrations of salts and minerals that can lead to kidney stone formation. Chronic dehydration is a major contributor to the development of kidney stones.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.