|
|
|
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
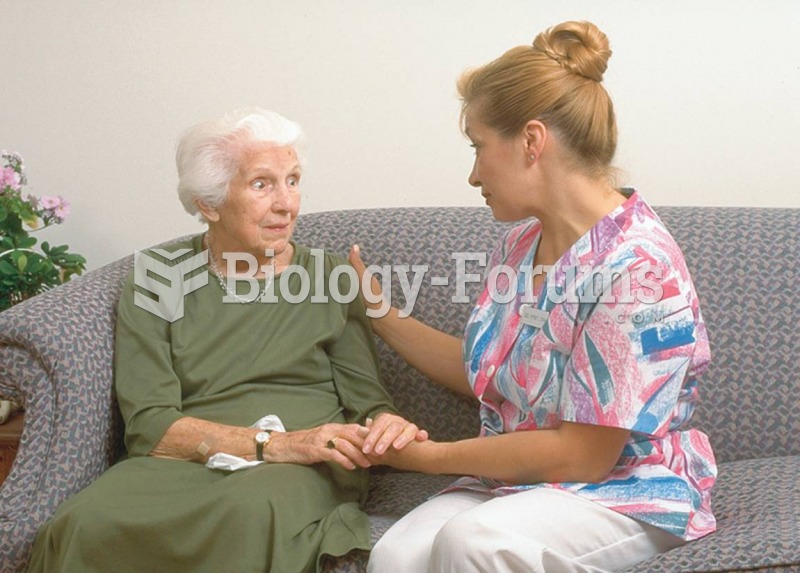
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.