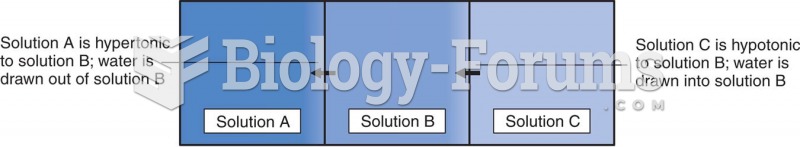
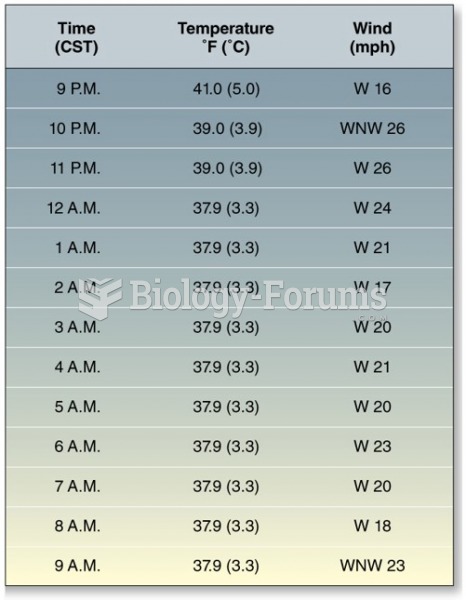
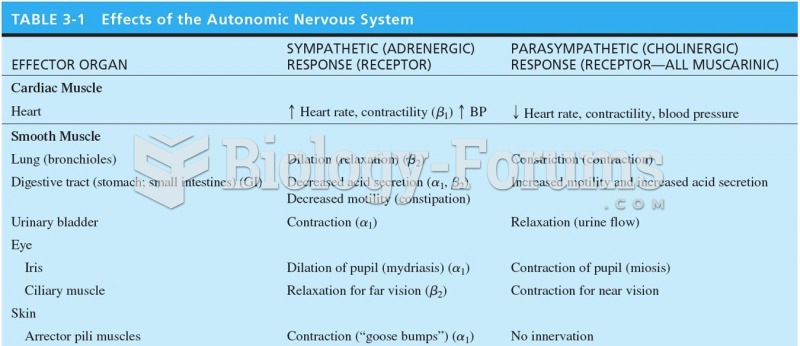
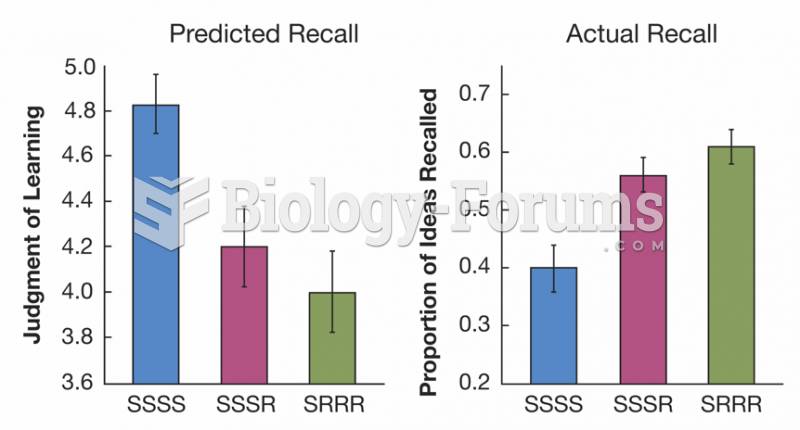
|
|
|
The first-known contraceptive was crocodile dung, used in Egypt in 2000 BC. Condoms were also reportedly used, made of animal bladders or intestines.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.