Answer to Question 1
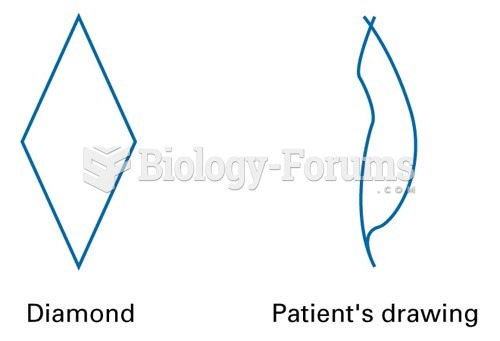
Apraxia is a deficit in the programming of musculature for voluntary movement in the absence of any muscular weakness or paralysis. There are different types of apraxia.
A client with limb apraxia does not have the ability to perform voluntary movements, including movement of the limbs. A client with this disorder might experience deficits in voluntarily using multiple objects to perform a sequence of acts upon request, such as making a sandwich.
A client with oral apraxia may have difficulty programming the facial and lingual muscles for acts that do not involve speech. For example, this person may not be able to blow out a candle.
Often the client with oral apraxia may also have verbal apraxia. Verbal apraxia is manifested by a deficit in programming the articulators of the sounds of speech. For instance, the person with verbal apraxia will make errors in the correct articulation of producing speech.
Answer to Question 2
The three major theories or models of speech control include the following:
1. The central control theory, which postulates that there is a master control system that dictates that muscle movements are based on the linguistic goal. The master control system administers muscle commands and accounts for the dominance of articulation for speech.
2. The dynamic or action theory models explain the physical properties involved in articulation. These theories account for the difficulties in articulation theory and explain how the system adapts to changes in the environment that might affect articulation.
3. The DIVA model of speech production refers to the directions into velocities of articulation. This model involves some forms of feedback concerning the accuracy of articulation. Feedback includes auditory feedback, tactile feedback, kinesthetic feedback, and feedback from external sources. The model establishes that learning takes place due to the feedback system of error correction. The DIVA model has started some clinical trials concerning a therapeutic use of the system, which is based on the use of a speech synthesizer. A major goal of the DIVA model is to enable people with neurological speech disabilities to express their thoughts via electrodes implanted in the brain and a speech synthesizer.