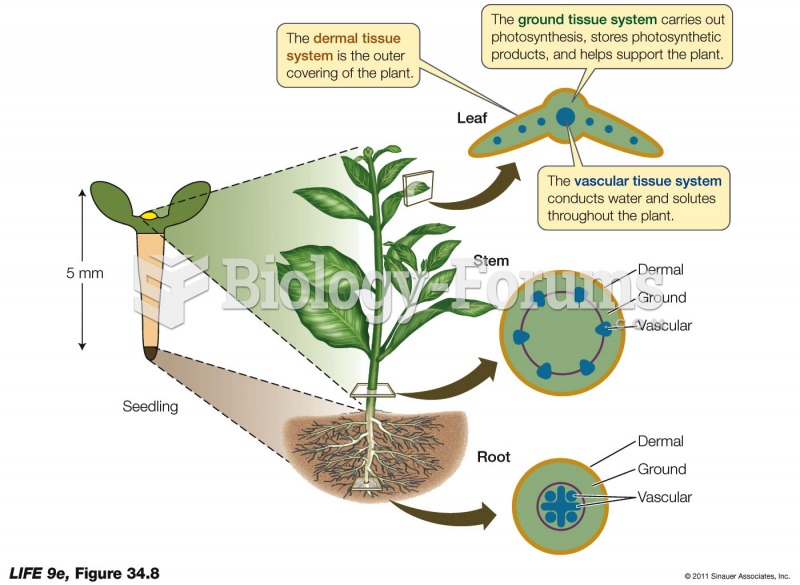
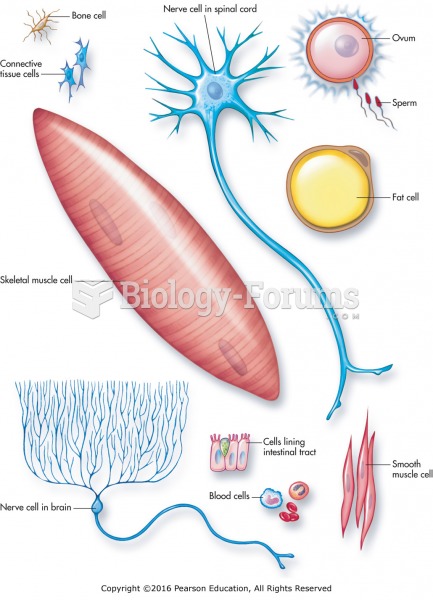
Answer to Question 1
The three major building blocks of the body are:
1. Organs: Collections of specific tissues that are organized into structures that are specialized to perform particular functions. Examples of organs include the kidneys, the heart, the liver, and the lungs.
2. Tissues: Collections or groups of similar cells that are specialized to perform specific functions. The four types of tissue include:
Epithelial tissue: refers to the outer or superficial layer of mucous membrane and the cells constituting the skin.
Connective tissue: probably the most complex of the categories of tissues, because it is specialized for the purposes of support. Connective tissue varies as a function of the intercellular material (matrix) surrounding it.
Muscular tissue: consists of voluntary (striated), involuntary (smooth), and cardiac muscle.
Nervous tissue: specialized for communication.
3. Systems: Combinations of organs that perform specific functions. In other words, systems of the body are groups of organs with functional unity. Organs can belong to more than one system. Examples of systems include the muscular system, the skeletal system, the respiratory system, the digestive system, the reproductive system, the urinary and endocrine systems, and the nervous system.
Answer to Question 2
Anatomical terms for body parts and tissues are primarily based on Greek and Latin. These languages were once universally used by early anatomists and medical practitioners. Today, anatomical and medical terms are still based on their ancient Greek and Latin roots.