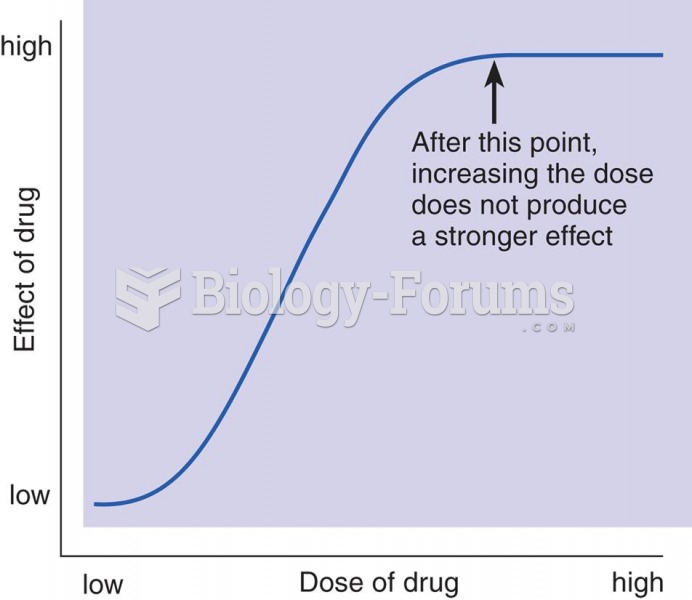
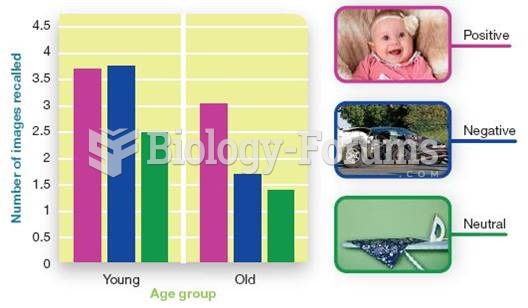
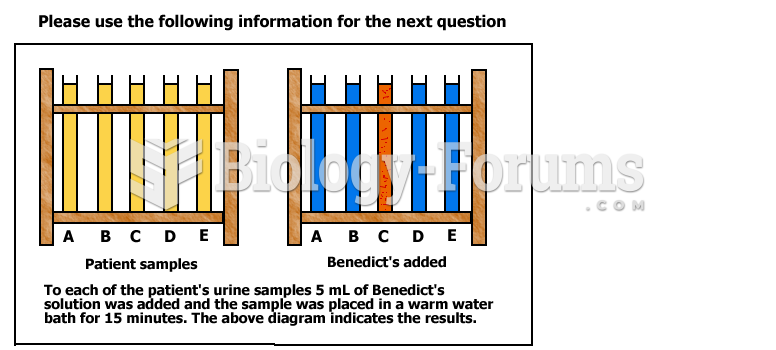
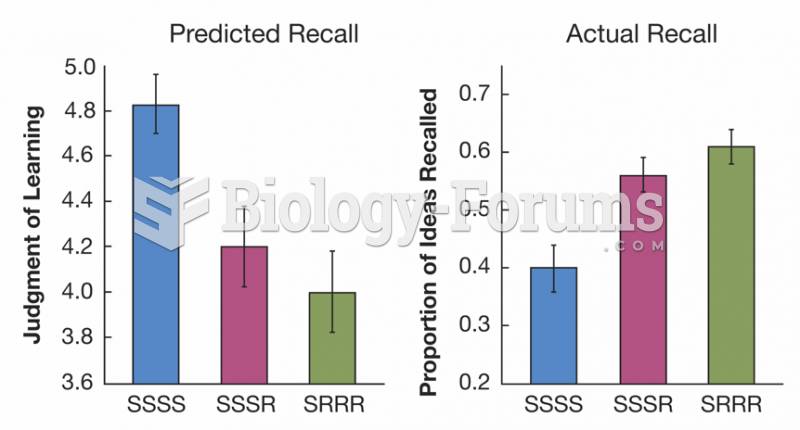
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The effects of organophosphate poisoning are referred to by using the abbreviations “SLUD” or “SLUDGE,” It stands for: salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, GI upset, and emesis.
Did you know?
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
Did you know?
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Did you know?
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Did you know?
Parkinson's disease is both chronic and progressive. This means that it persists over a long period of time and that its symptoms grow worse over time.